Page 473 - Read Online
P. 473
Maner et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:37 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.60 Page 25 of 40
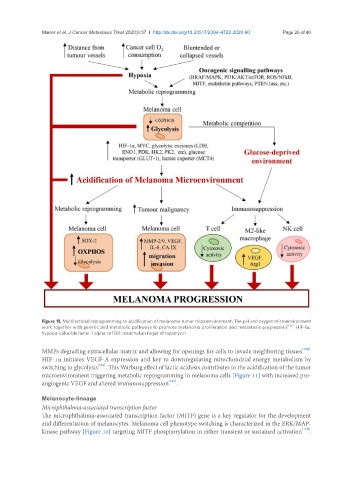
Figure 11. Multifactorial reprogramming to acidification of melanoma tumor microenvironment. The pH and oxygen microenvironment
work together with genetic and metabolic pathways to promote melanoma proliferation and metastasis progression [176] . HIF-1α:
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin
MMPs degrading extracellular matrix and allowing for openings for cells to invade neighboring tissues [174] .
HIF-1α initiates VEGF-A expression and key to downregulating mitochondrial energy metabolism by
switching to glycolysis [163] . This Warburg effect of lactic acidosis contributes to the acidification of the tumor
microenvironment triggering metabolic reprogramming in melanoma cells [Figure 11] with increased pro-
angiogenic VEGF and altered immunosuppression [167] .
Melanocyte-lineage
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor
The microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) gene is a key regulator for the development
and differentiation of melanocytes. Melanoma cell phenotype switching is characterized in the ERK/MAP-
kinase pathway [Figure 10] targeting MITF phosphorylation in either transient or sustained activation [177] .