Page 472 - Read Online
P. 472
Page 24 of 40 Maner et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:37 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.60
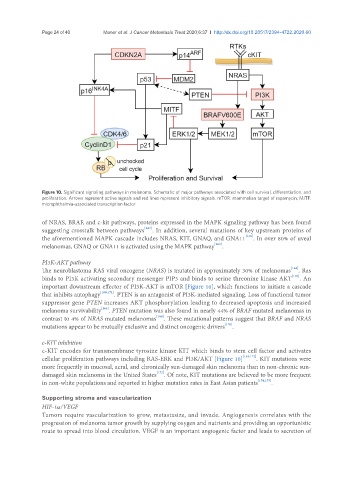
Figure 10. Significant signaling pathways in melanoma. Schematic of major pathways associated with cell survival, differentiation, and
proliferation. Arrows represent active signals and red lines represent inhibitory signals. mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; MITF:
microphthalmia-associated transcription factor
of NRAS, BRAF, and c-kit pathways, proteins expressed in the MAPK signaling pathway has been found
suggesting crosstalk between pathways [167] . In addition, several mutations of key upstream proteins of
the aforementioned MAPK cascade includes NRAS, KIT, GNAQ, and GNA11 [168] . In over 80% of uveal
melanomas, GNAQ or GNA11 is activated using the MAPK pathway [169] .
PI3K-AKT pathway
The neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene (NRAS) is mutated in approximately 30% of melanomas [168] . Ras
binds to PI3K activating secondary messenger PIP3 and binds to serine threonine kinase AKT [170] . An
important downstream effector of PI3K-AKT is mTOR [Figure 10], which functions to initiate a cascade
that inhibits autophagy [160,171] . PTEN is an antagonist of PI3K-mediated signaling. Loss of functional tumor
suppressor gene PTEN increases AKT phosphorylation leading to decreased apoptosis and increased
melanoma survivability [165] . PTEN mutation was also found in nearly 44% of BRAF mutated melanomas in
contrast to 4% of NRAS mutated melanomas [168] . These mutational patterns suggest that BRAF and NRAS
mutations appear to be mutually exclusive and distinct oncogenic drivers [170] .
c-KIT inhibition
c-KIT encodes for transmembrane tyrosine kinase KIT which binds to stem cell factor and activates
cellular proliferation pathways including RAS-ERK and PI3K/AKT [Figure 10] [162,172] . KIT mutations were
more frequently in mucosal, acral, and chronically sun-damaged skin melanoma than in non-chronic sun-
damaged skin melanoma in the United States [173] . Of note, KIT mutations are believed to be more frequent
in non-white populations and reported in higher mutation rates in East Asian patients [174,175] .
Supporting stroma and vascularization
HIF-1α/VEGF
Tumors require vascularization to grow, metastasize, and invade. Angiogenesis correlates with the
progression of melanoma tumor growth by supplying oxygen and nutrients and providing an opportunistic
route to spread into blood circulation. VEGF is an important angiogenic factor and leads to secretion of