Page 253 - Read Online
P. 253
Page 6 of 7 Mascarenhas et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:23 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.52
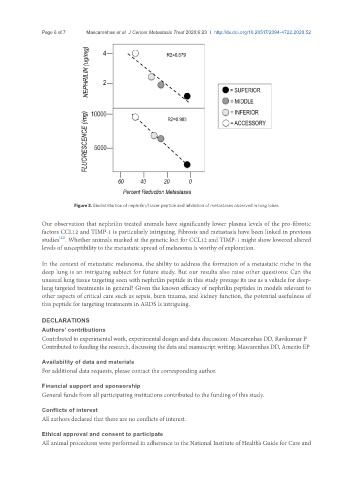
Figure 3. Biodistribution of nephrilin/tracer peptide and inhibition of metastases observed in lung lobes
Our observation that nephrilin treated animals have significantly lower plasma levels of the pro-fibrotic
factors CCL12 and TIMP-1 is particularly intriguing. Fibrosis and metastasis have been linked in previous
[22]
studies . Whether animals marked at the genetic loci for CCL12 and TIMP-1 might show lowered altered
levels of susceptibility to the metastatic spread of melanoma is worthy of exploration.
In the context of metastatic melanoma, the ability to address the formation of a metastatic niche in the
deep lung is an intriguing subject for future study. But our results also raise other questions: Can the
unusual lung tissue targeting seen with nephrilin peptide in this study presage its use as a vehicle for deep-
lung targeted treatments in general? Given the known efficacy of nephrilin peptides in models relevant to
other aspects of critical care such as sepsis, burn trauma, and kidney function, the potential usefulness of
this peptide for targeting treatments in ARDS is intriguing.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Contributed to experimental work, experimental design and data discussion: Mascarenhas DD, Ravikumar P
Contributed to funding the research, discussing the data and manuscript writing: Mascarenhas DD, Amento EP
Availability of data and materials
For additional data requests, please contact the corresponding author.
Financial support and sponsorship
General funds from all participating institutions contributed to the funding of this study.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All animal procedures were performed in adherence to the National Institute of Health’s Guide for Care and