Page 252 - Read Online
P. 252
Mascarenhas et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:22 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.52 Page 5 of 7
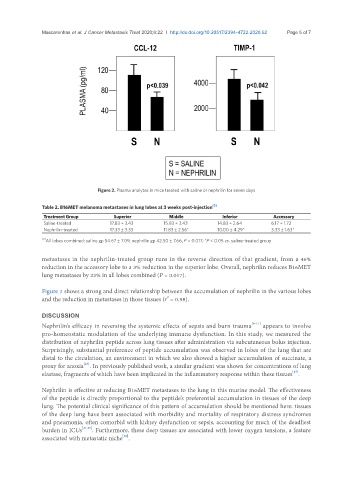
Figure 2. Plasma analytes in mice treated with saline or nephrilin for seven days
Table 2. B16MET melanoma metastases in lung lobes at 3 weeks post-injection [2]
Treatment Group Superior Middle Inferior Accessory
Saline-treated 17.83 ± 3.43 15.83 ± 3.43 14.83 ± 2.64 6.17 ± 1.72
Nephrilin-treated 17.33 ± 3.33 11.83 ± 2.56* 10.00 ± 4.29* 3.33 ± 1.63*
[2] All lobes combined: saline gp 54.67 ± 7.09, nephrilin gp 42.50 ± 7.66, P = 0.017; *P < 0.05 vs. saline-treated group
metastases in the nephrilin-treated group runs in the reverse direction of that gradient, from a 46%
reduction in the accessory lobe to a 3% reduction in the superior lobe. Overall, nephrilin reduces B16MET
lung metastases by 22% in all lobes combined (P = 0.017).
Figure 3 shows a strong and direct relationship between the accumulation of nephrilin in the various lobes
2
and the reduction in metastases in those tissues (r = 0.98).
DISCUSSION
Nephrilin’s efficacy in reversing the systemic effects of sepsis and burn trauma [9-11] appears to involve
pro-homeostatic modulation of the underlying immune dysfunction. In this study, we measured the
distribution of nephrilin peptide across lung tissues after administration via subcutaneous bolus injection.
Surprisingly, substantial preference of peptide accumulation was observed in lobes of the lung that are
distal to the circulation, an environment in which we also showed a higher accumulation of succinate, a
proxy for anoxia . In previously published work, a similar gradient was shown for concentrations of lung
[23]
[17]
elastase, fragments of which have been implicated in the inflammatory response within these tissues .
Nephrilin is effective at reducing B16MET metastases to the lung in this murine model. The effectiveness
of the peptide is directly proportional to the peptide’s preferential accumulation in tissues of the deep
lung. The potential clinical significance of this pattern of accumulation should be mentioned here: tissues
of the deep lung have been associated with morbidity and mortality of respiratory distress syndromes
and pneumonia, often comorbid with kidney dysfunction or sepsis, accounting for much of the deadliest
burden in ICUs [24,25] . Furthermore, these deep tissues are associated with lower oxygen tensions, a feature
[26]
associated with metastatic niche .