Page 624 - Read Online
P. 624
Page 12 of 24 Peyvandi et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:44 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.16
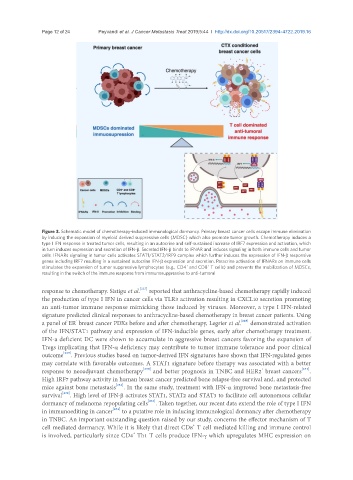
Figure 3. Schematic model of chemotherapy-induced immunological dormancy. Primary breast cancer cells escape immune elimination
by inducing the expansion of myeloid derived suppressive cells (MDSC) which also promote tumor growth. Chemotherapy induces a
type I IFN response in treated tumor cells, resulting in an autocrine and self-sustained increase of IRF7 expression and activation, which
in turn induces expression and secretion of IFN-β. Secreted IFN-β binds to IFNAR and induces signaling in both immune cells and tumor
cells. IFNARs signaling in tumor cells activates STAT1/STAT2/IRF9 complex which further induces the expression of IFN-β responsive
genes including IRF7 resulting in a sustained autocrine IFN-β expression and secretion. Paracrine activation of IFNARs on immune cells
+
+
stimulates the expansion of tumor suppressive lymphocytes (e.g., CD4 and CD8 T cells) and prevents the mobilization of MDSCs,
resulting in the switch of the immune response from immunosuppressive to anti-tumoral
[227]
response to chemotherapy. Sistigu et al. reported that anthracycline-based chemotherapy rapidly induced
the production of type I IFN in cancer cells via TLR3 activation resulting in CXCL10 secretion promoting
an anti-tumor immune response mimicking those induced by viruses. Moreover, a type I IFN-related
signature predicted clinical responses to anthracycline-based chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Using
-
[228]
a panel of ER breast cancer PDXs before and after chemotherapy, Legrier et al. demonstrated activation
of the IFN/STAT1 pathway and expression of IFN-inducible genes, early after chemotherapy treatment.
IFN-a deficient DC were shown to accumulate in aggressive breast cancers favoring the expansion of
Tregs implicating that IFN-α deficiency may contribute to tumor immune tolerance and poor clinical
outcome [229] . Previous studies based on tumor-derived IFN signatures have shown that IFN-regulated genes
may correlate with favorable outcomes. A STAT1 signature before therapy was associated with a better
+
response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy [230] and better prognosis in TNBC and HER2 breast cancers [231] .
High IRF7 pathway activity in human breast cancer predicted bone relapse-free survival and, and protected
mice against bone metastasis [232] . In the same study, treatment with IFN-α improved bone metastasis-free
survival [232] . High level of IFN-β activates STAT1, STAT2 and STAT3 to facilitate cell autonomous cellular
dormancy of melanoma repopulating cells [233] . Taken together, our recent data extend the role of type I IFN
in immunoediting in cancer [234] to a putative role in inducing immunological dormancy after chemotherapy
in TNBC. An important outstanding question raised by our study, concerns the effector mechanism of T
+
cell mediated dormancy. While it is likely that direct CD8 T cell mediated killing and immune control
+
is involved, particularly since CD4 Th1 T cells produce IFN-γ which upregulates MHC expression on