Page 464 - Read Online
P. 464
Page 16 of 25 Kondapuram et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.105
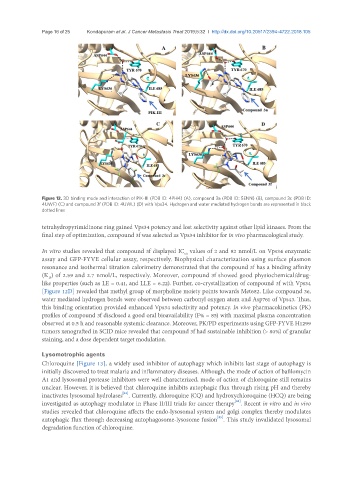
Figure 12. 3D binding mode and interaction of PIK-III (PDB ID: 4PH4) (A), compound 3a (PDB ID: 5ENN) (B), compound 3c (PDB ID:
4UWF) (C) and compound 3f (PDB ID: 4UWL) (D) with Vps34. Hydrogen and water mediated hydrogen bonds are represented in black
dotted lines
tetrahydropyrimidinone ring gained Vps34 potency and lost selectivity against other lipid kinases. From the
final step of optimization, compound 3f was selected as Vps34 inhibitor for in vivo pharmacological study.
In vitro studies revealed that compound 3f displayed IC values of 2 and 82 nmol/L on Vps34 enzymatic
50
assay and GFP-FYVE cellular assay, respectively. Biophysical characterization using surface plasmon
resonance and isothermal titration calorimetry demonstrated that the compound 3f has a binding affinity
(K ) of 2.59 and 2.7 nmol/L, respectively. Moreover, compound 3f showed good physiochemical/drug-
D
like properties (such as LE = 0.41, and LLE = 6.22). Further, co-crystallization of compound 3f with Vps34
[Figure 12D] revealed that methyl group of morpholine moiety points towards Met682. Like compound 3e,
water mediated hydrogen bonds were observed between carbonyl oxygen atom and Asp761 of Vps43. Thus,
this binding orientation provided enhanced Vps34 selectivity and potency. In vivo pharmacokinetics (PK)
profiles of compound 3f disclosed a good oral bioavailability (F% = 85) with maximal plasma concentration
observed at 0.5 h and reasonable systemic clearance. Moreover, PK/PD experiments using GFP-FYVE H1299
tumors xenografted in SCID mice revealed that compound 3f had sustainable inhibition (> 80%) of granular
staining, and a dose dependent target modulation.
Lysomotrophic agents
Chloroquine [Figure 13], a widely used inhibitor of autophagy which inhibits last stage of autophagy is
initially discovered to treat malaria and inflammatory diseases. Although, the mode of action of bafilomycin
A1 and lysosomal protease inhibitors were well characterized, mode of action of chloroquine still remains
unclear. However, it is believed that chloroquine inhibits autophagic flux through rising pH and thereby
[83]
inactivates lysosomal hydrolases . Currently, chloroquine (CQ) and hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) are being
investigated as autophagy modulator in Phase II/III trials for cancer therapy . Recent in vitro and in vivo
[84]
studies revealed that chloroquine affects the endo-lysosomal system and golgi complex thereby modulates
[85]
autophagic flux through decreasing autophagosome-lysosome fusion . This study invalidated lysosomal
degradation function of chloroquine.