Page 456 - Read Online
P. 456
Page 8 of 25 Kondapuram et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.105
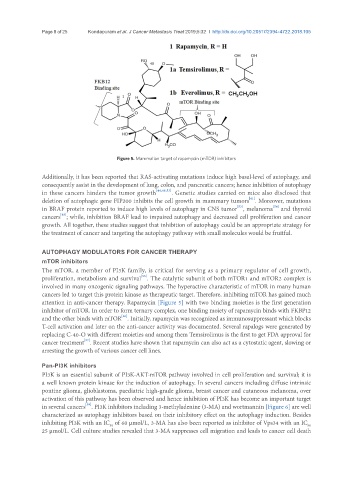
Figure 5. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors
Additionally, it has been reported that RAS-activating mutations induce high basal-level of autophagy, and
consequently assist in the development of lung, colon, and pancreatic cancers; hence inhibition of autophagy
in these cancers hinders the tumor growth [44,48,53] . Genetic studies carried on mice also disclosed that
[41]
deletion of autophagic gene FIP200 inhibits the cell growth in mammary tumors . Moreover, mutations
[53]
[54]
in BRAF protein reported to induce high levels of autophagy in CNS tumor , melanoma and thyroid
[45]
cancers ; while, inhibition BRAF lead to impaired autophagy and decreased cell proliferation and cancer
growth. All together, these studies suggest that inhibition of autophagy could be an appropriate strategy for
the treatment of cancer and targeting the autophagy pathway with small molecules would be fruitful.
AUTOPHAGY MODULATORS FOR CANCER THERAPY
mTOR inhibitors
The mTOR, a member of PI3K family, is critical for serving as a primary regulator of cell growth,
[55]
proliferation, metabolism and survival . The catalytic subunit of both mTOR1 and mTOR2 complex is
involved in many oncogenic signaling pathways. The hyperactive characteristic of mTOR in many human
cancers led to target this protein kinase as therapeutic target. Therefore, inhibiting mTOR has gained much
attention in anti-cancer therapy. Rapamycin [Figure 5] with two binding moieties is the first generation
inhibitor of mTOR. In order to form ternary complex, one binding moiety of rapamycin binds with FKBP12
[56]
and the other binds with mTOR . Initially, rapamycin was recognized as immunosuppressant which blocks
T-cell activation and later on the anti-cancer activity was documented. Several rapalogs were generated by
replacing C-40-O with different moieties and among them Temsirolimus is the first to get FDA approval for
[57]
cancer treatment . Recent studies have shown that rapamycin can also act as a cytostatic agent, slowing or
arresting the growth of various cancer cell lines.
Pan-PI3K inhibitors
PI3K is an essential subunit of PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway involved in cell proliferation and survival; it is
a well known protein kinase for the induction of autophagy. In several cancers including diffuse intrinsic
pontine glioma, glioblastoma, paediatric high-grade glioma, breast cancer and cutaneous melanoma, over
activation of this pathway has been observed and hence inhibition of PI3K has become an important target
[58]
in several cancers . PI3K inhibitors including 3-methyladenine (3-MA) and wortmannin [Figure 6] are well
characterized as autophagy inhibitors based on their inhibitory effect on the autophagy induction. Besides
inhibiting PI3K with an IC of 60 µmol/L, 3-MA has also been reported as inhibitor of Vps34 with an IC 50
50
25 µmol/L. Cell culture studies revealed that 3-MA suppresses cell migration and leads to cancer cell death