Page 453 - Read Online
P. 453
Kondapuram et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:32 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.105 Page 5 of 25
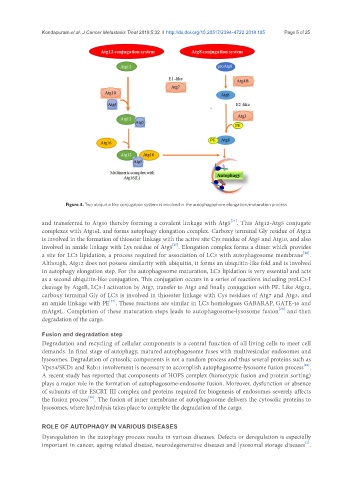
Figure 4. Two ubiquitin like conjugation system is involved in the autophagophore elongation/maturation process
[24]
and transferred to Atg10 thereby forming a covalent linkage with Atg5 . This Atg12-Atg5 conjugate
complexes with Atg16L and forms autophagy elongation complex. Carboxy terminal Gly residue of Atg12
is involved in the formation of thioester linkage with the active site Cys residue of Atg5 and Atg10, and also
[25]
involved in amide linkage with Lys residue of Atg5 . Elongation complex forms a dimer which provides
[26]
a site for LC3 lipidation, a process required for association of LC3 with autophagosome membrane .
Although, Atg12 does not possess similarity with ubiquitin, it forms an ubiquitin-like fold and is involved
in autophagy elongation step. For the autophagosome maturation, LC3 lipidation is very essential and acts
as a second ubiquitin-like conjugation. This conjugation occurs in a series of reactions including proLC3-I
cleavage by Atg4B, LC3-I activation by Atg7, transfer to Atg3 and finally conjugation with PE. Like Atg12,
carboxy terminal Gly of LC3 is involved in thioester linkage with Cys residues of Atg7 and Atg3, and
[27]
an amide linkage with PE . These reactions are similar in LC3 homologues GABARAP, GATE-16 and
[28]
mAtg8L. Completion of these maturation steps leads to autophagosome-lysosome fusion and then
degradation of the cargo.
Fusion and degradation step
Degradation and recycling of cellular components is a central function of all living cells to meet cell
demands. In final stage of autophagy, matured autophagosome fuses with multivesicular endosomes and
lysosomes. Degradation of cytosolic components is not a random process and thus several proteins such as
[29]
Vps34/SKD1 and Rab11 involvement is necessary to accomplish autophagosome-lysosome fusion process .
A recent study has reported that components of HOPS complex (homotypic fusion and protein sorting)
plays a major role in the formation of autophagosome-endosome fusion. Moreover, dysfunction or absence
of subunits of the ESCRT III complex and proteins required for biogenesis of endosomes severely affects
[30]
the fusion process . The fusion of inner membrane of autophagosome delivers the cytosolic proteins to
lysosomes, where hydrolysis takes place to complete the degradation of the cargo.
ROLE OF AUTOPHAGY IN VARIOUS DISEASES
Dysregulation in the autophagy process results in various diseases. Defects or deregulation is especially
[2]
important in cancer, ageing related disease, neurodegenerative diseases and lysosomal storage diseases .