Page 234 - Read Online
P. 234
Page 8 of 12 Park et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:17 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.84
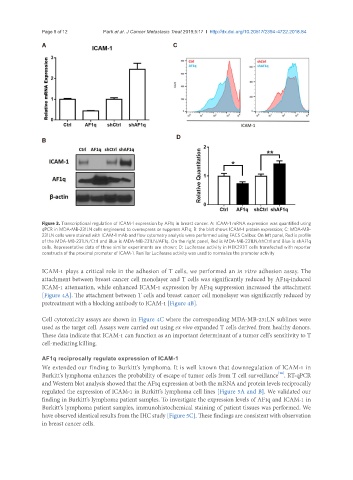
A C
D
B
Figure 3. Transcriptional regulation of ICAM-1 expression by AF1q in breast cancer. A: ICAM-1 mRNA expression was quantified using
qPCR in MDA-MB-231LN cells engineered to overexpress or suppress AF1q; B: the blot shows ICAM-1 protein expression; C: MDA-MB-
231LN cells were stained with ICAM-1 mAb and flow cytometry analysis were performed using FACS Calibur. On left panel, Red is profile
of the MDA-MB-231LN/Ctrl and Blue is MDA-MB-231LN/AF1q. On the right panel, Red is MDA-MB-231LN/shCtrl and Blue is shAF1q
cells. Representative data of three similar experiments are shown; D: Luciferase activity in HEK293T cells transfected with reporter
constructs of the proximal promoter of ICAM-1. Renillar Luciferase activity was used to normalize the promoter activity
ICAM-1 plays a critical role in the adhesion of T cells, we performed an in vitro adhesion assay. The
attachment between breast cancer cell monolayer and T cells was significantly reduced by AF1q-induced
ICAM-1 attenuation, while enhanced ICAM-1 expression by AF1q suppression increased the attachment
[Figure 4A]. The attachment between T cells and breast cancer cell monolayer was significantly reduced by
pretreatment with a blocking antibody to ICAM-1 [Figure 4B].
Cell cytotoxicity assays are shown in Figure 4C where the corresponding MDA-MB-231LN sublines were
used as the target cell. Assays were carried out using ex vivo expanded T cells derived from healthy donors.
These data indicate that ICAM-1 can function as an important determinant of a tumor cell’s sensitivity to T
cell-mediating killing.
AF1q reciprocally regulate expression of ICAM-1
We extended our finding to Burkitt’s lymphoma. It is well known that downregulation of ICAM-1 in
[16]
Burkitt’s lymphoma enhances the probability of escape of tumor cells from T cell surveillance . RT-qPCR
and Western blot analysis showed that the AF1q expression at both the mRNA and protein levels reciprocally
regulated the expression of ICAM-1 in Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines [Figure 5A and B]. We validated our
finding in Burkitt’s lymphoma patient samples. To investigate the expression levels of AF1q and ICAM-1 in
Burkitt’s lymphoma patient samples, immunohistochemical staining of patient tissues was performed. We
have observed identical results from the IHC study [Figure 5C]. These findings are consistent with observation
in breast cancer cells.