Page 202 - Read Online
P. 202
Page 8 of 13 Suominen et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:14 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.64
A
B C
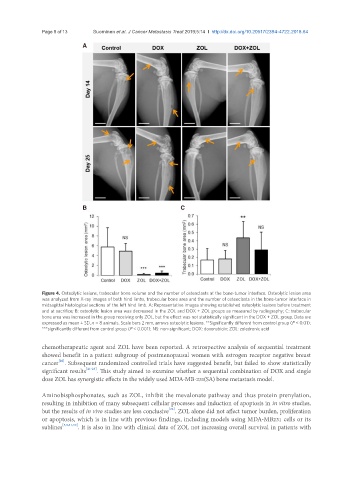
Figure 4. Osteolytic lesions, trabecular bone volume and the number of osteoclasts at the bone-tumor interface. Osteolytic lesion area
was analyzed from X-ray images of both hind limbs, trabecular bone area and the number of osteoclasts in the bone-tumor interface in
midsagittal histological sections of the left hind limb. A: Representative images showing established osteolytic lesions before treatment
and at sacrifice; B: osteolytic lesion area was decreased in the ZOL and DOX + ZOL groups as measured by radiography; C: trabecular
bone area was increased in the group receiving only ZOL, but the effect was not statistically significant in the DOX + ZOL group. Data are
expressed as mean ± SD, n = 8 animals. Scale bars 2 mm, arrows osteolytic lesions. **Significantly different from control group (P < 0.01);
***significantly different from control group (P < 0.001); NS: non-significant; DOX: doxorubicin; ZOL: zoledronic acid
chemotherapeutic agent and ZOL have been reported. A retrospective analysis of sequential treatment
showed benefit in a patient subgroup of postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor negative breast
[20]
cancer . Subsequent randomized controlled trials have suggested benefit, but failed to show statistically
significant results [21-23] . This study aimed to examine whether a sequential combination of DOX and single
dose ZOL has synergistic effects in the widely used MDA-MB-231(SA) bone metastasis model.
Aminobisphosphonates, such as ZOL, inhibit the mevalonate pathway and thus protein prenylation,
resulting in inhibition of many subsequent cellular processes and induction of apoptosis in in vitro studies,
but the results of in vivo studies are less conclusive . ZOL alone did not affect tumor burden, proliferation
[24]
or apoptosis, which is in line with previous findings, including models using MDA-MB231 cells or its
sublines [5,8,11,12] . It is also in line with clinical data of ZOL not increasing overall survival in patients with