Page 372 - Read Online
P. 372
Sommariva Liver metastases and HIPEC
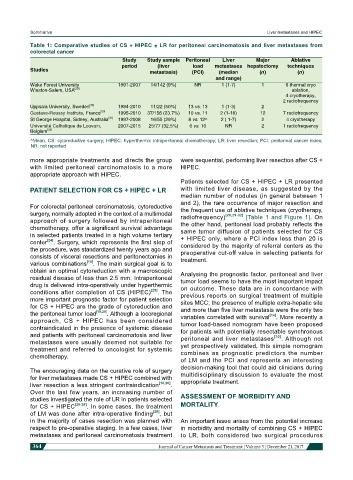
Table 1: Comparative studies of CS + HIPEC ± LR for peritoneal carcinomatosis and liver metastases from
colorectal cancer
Study Study sample Peritoneal Liver Major Ablative
period (liver load metastases hepatectomy techniques
Studies metastasis) (PCI) (median (n) (n)
and range)
Wake Forest University 1991-2007 14/142 (9%) NR 1 (1-7) 1 6 thermal cryo
Winston-Salem, USA [29] ablation,
4 cryotherapy,
2 radiofrequency
Uppsala University, Sweden [30] 1994-2010 11/22 (50%) 13 vs. 13 1 (1-3) 2 -
Gustave-Roussy Institute, France [20] 1995-2010 37/156 (23.7%) 10 vs. 11 2 (1-16) 12 7 radiofrequency
St George Hospital, Sidney, Australia [31] 1997-2008 16/55 (29%) 8 vs. 12^ 2 ( 1-7) 2 4 cryotherapy
Université Catholique de Louvain, 2007-2015 25/77 (32.5%) 6 vs. 10 NR 2 1 radiofrequency
Belgium [32]
^Mean. CS: cytoreductive surgery; HIPEC: hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy; LR: liver resection; PCI: peritoneal cancer index;
NR: not reported
more appropriate treatments and directs the group were sequential, performing liver resection after CS +
with limited peritoneal carcinomatosis to a more HIPEC.
appropriate approach with HIPEC.
Patients selected for CS + HIPEC + LR presented
PATIENT SELECTION FOR CS + HIPEC + LR with limited liver disease, as suggested by the
median number of nodules (in general between 1
and 2), the rare occurrence of major resection and
For colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis, cytoreductive the frequent use of ablative techniques (cryotherapy,
surgery, normally adopted in the context of a multimodal radiofrequency) [20,29-32] [Table 1 and Figure 1]. On
approach of surgery followed by intraperitoneal the other hand, peritoneal load probably reflects the
chemotherapy, offer a significant survival advantage same tumor diffusion of patients selected for CS
in selected patients treated in a high volume tertiary + HIPEC only, where a PCI index less than 20 is
center [24] . Surgery, which represents the first step of considered by the majority of referral centers as the
the procedure, was standardized twenty years ago and preoperative cut-off value in selecting patients for
consists of visceral resections and peritonectomies in treatment.
various combinations [10] . The main surgical goal is to
obtain an optimal cytoreduction with a macroscopic Analysing the prognostic factor, peritoneal and liver
residual disease of less than 2.5 mm. Intraperitoneal tumor load seems to have the most important impact
drug is delivered intra-operatively under hyperthermic on outcome. These data are in concordance with
conditions after completion of CS (HIPEC) [25] . The previous reports on surgical treatment of multiple
more important prognostic factor for patient selection sites MCC; the presence of multiple extra-hepatic site
for CS + HIPEC are the grade of cytoreduction and and more than five liver metastasis were the only two
the peritoneal tumor load [19,20] . Although a locoregional variables correlated with survival [14] . More recently a
approach, CS + HIPEC has been considered tumor load-based nomogram have been proposed
contraindicated in the presence of systemic disease for patients with potentially resectable synchronous
and patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis and liver peritoneal and liver metastases [20] . Although not
metastases were usually deemed not suitable for
treatment and referred to oncologist for systemic yet prospectively validated, this simple nomogram
chemotherapy. combines as prognostic predictors the number
of LM and the PCI and represents an interesting
decision-making tool that could aid clinicians during
The encouraging data on the curative role of surgery
for liver metastases made CS + HIPEC combined with multidisciplinary discussion to evaluate the most
liver resection a less stringent contraindication [18,20] . appropriate treatment.
Over the last few years, an increasing number of
studies investigated the role of LR in patients selected ASSESSMENT OF MORBIDITY AND
for CS + HIPEC [26-28] . In some cases, the treatment MORTALITY
of LM was done after intra-operative finding [28] , but
in the majority of cases resection was planned with An important issue arises from the potential increase
respect to pre-operative staging. In a few cases, liver in morbidity and mortality of combining CS + HIPEC
metastases and peritoneal carcinomatosis treatment to LR, both considered two surgical procedures
364 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ December 21, 2017