Page 85 - Read Online
P. 85
Figure 4: Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and intra-
operative ultrasound/contrast-enhanced US: High grade lesion can be
compared, between the technologies. iUS an be used for the localization for
most of the lesion, but with better results with cystic/heterogeneous tumors.
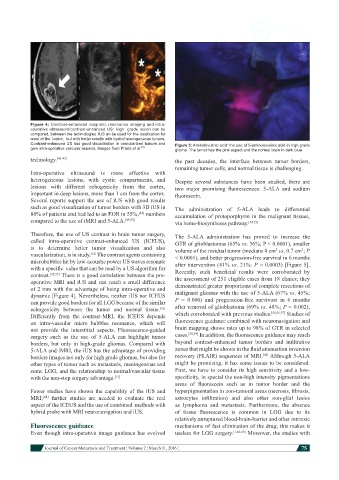
Contrast-enhanced US has good visualization in vascularized tumors and Figure 5: Aminolevulinic acid: the use of 5-aminolevulinic acid in high grade
give intra-operative vascular aspects. Images from Prada et al. [51] glioma. The tumor has the pink aspect and the normal brain in dark blue
technology. [45-47] the past decades, the interface between tumor borders,
remaining tumor cells, and normal tissue is challenging.
Intra-operative ultrasound is more effective with
heterogeneous lesions, with cystic compartments, and Despite several substances have been studied, there are
lesions with different echogenicity from the cortex, two major promising fluorescences: 5-ALA and sodium
important in deep lesions, more than 1 cm from the cortex. fluorescein.
Several reports support the use of iUS with good results
such as good visualization of tumor borders with 3D iUS in The administration of 5-ALA leads to differential
88% of patients and had led to an EOR in 55%, numbers accumulation of protoporphyrin in the malignant tissues,
[48]
compared to the use of iMRI and 5-ALA. [49,50] via heme-biosyntheses pathway. [54,55]
Therefore, the use of US contrast in brain tumor surgery, The 5-ALA administration has proved to increase the
called intra-operative contrast-enhanced US (ICEUS), GTR of glioblastomas (65% vs. 36%; P < 0.0001), smaller
is to determine better tumor visualization and also volume of the residual tumor (medians 0 cm vs. 0.7 cm ; P
3
3
vascularization, is in study. The contrast agents containing < 0.0001), and better progression-free survival in 6 months
[51]
microbubbles hit by low-acoustic power US waves resonate after intervention (41% vs. 21%: P = 0.0003) [Figure 5].
with a specific value that can be read by a US algorithm for Recently, such beneficial results were corroborated by
contrast. [52,53] There is a good correlation between the pre- the assessment of 251 eligible cases from 18 clinics; they
operative MRI and iUS and can reach a small difference demonstrated greater proportions of complete resections of
of 2 mm with the advantage of being intra-operative and
dynamic [Figure 4]. Nevertheless, neither iUS nor ICEUS malignant gliomas with the use of 5-ALA (67% vs. 45%;
can provide good borders for all LGG because of the similar P = 0.000) and progression-free survivors in 6 months
echogenicity between the tumor and normal tissue. after removal of glioblastoma (69% vs. 48%; P = 0.002),
[51]
[54,56,57]
Differently from the contrast-MRI, the ICEUS depends which corroborated with previous studies. Studies of
on intra-vascular micro bubbles resonance, which will fluorescence guidance combined with neuronavigation and
not provide the interstitial aspects. Fluorescence-guided brain mapping shows rates up to 98% of GTR in selected
surgery such as the use of 5-ALA can highlight tumor cases. [58,59] In addition, the fluorescence guidance may reach
borders, but only in high-grade gliomas. Compared with beyond contrast-enhanced tumor borders and infiltrative
5-ALA and iMRI, the iUS has the advantage of providing zones that might be shown in the fluid attenuation inversion
[42]
borders images not only for high grade gliomas, but also for recovery (FLAIR) sequences of MRI. Although 5-ALA
other types of tumor such as metastasis, meningeomas and might be promising, it has some issues to be considered.
some LGG, and the relationship to normal/vascular tissue First, we have to consider its high sensitivity and a low-
with the non-stop surgery advantage. [51] specificity, in special the non-high intensity pigmentations
areas of fluorescein such as in tumor border and the
Fewer studies have shown the capability of the iUS and hyperpigmentation in non-tumoral areas (necrosis, fibrosis,
MRI; further studies are needed to evaluate the real astrocytes infiltration) and also other non-glial lesios
[48]
aspect of the ICEUS and the use of combined methods with as lymphoma and metastasis. Furthermore, the absence
hybrid probe with MRI neuronavigation and iUS. of tissue fluorescence is common in LGG due to its
relatively unruptured blood-brain-barrier and other intrinsic
Fluorescence guidance mechanisms of fast elimination of the drug; this makes it
Even though intra-operative image guidance has evolved useless for LGG surgery. [1,60-63] Moreover, the studies with
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ March 11, 2016 ¦ 75