Page 399 - Read Online
P. 399
Petracco et al. Solitary fibrous tumor of the bladder
hospital. He underwent an echographic investigation
that showed only grade 1-2 hydronephrosis. Moreover,
leucocytosis and elevated C-reactive protein was
observed. An expulsion therapy was performed.
After 1 week, a computed tomography scan showed
hydronephrosis with a 10 mm × 8 mm ureteral
calculus located 4 cm from the bladder neck. The
patient underwent an endoscopic lithotripsy. During
the procedure, a 4 mm bladder nodule was seen on
the mucosa surface, thus removed by the urologist
and submitted for histologic examination.
This showed a mesenchymal proliferation with
low cellularity [Figure 1], without atypia [Figure 2]
and a mitotic index below 1/10 high power field.
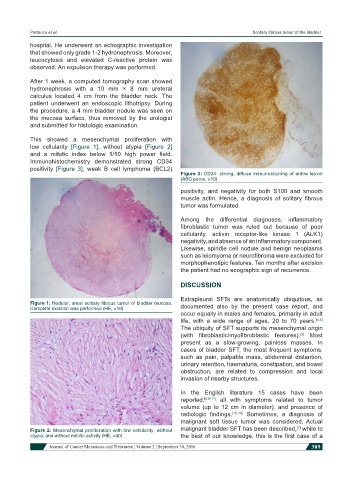
Immunohistochemistry demonstrated strong CD34
positivity [Figure 3], weak B cell lymphoma (BCL2)
Figure 3: CD34: strong, diffuse immunostaining of entire lesion
(ABC perox, ×10)
positivity, and negativity for both S100 and smooth
muscle actin. Hence, a diagnosis of solitary fibrous
tumor was formulated.
Among the differential diagnoses, inflammatory
fibroblastic tumor was ruled out because of poor
cellularity, activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1)
negativity, and absence of an inflammatory component.
Likewise, spindle cell nodule and benign neoplasms
such as leiomyoma or neurofibroma were excluded for
morphophenotipic features. Ten months after excision
the patient had no ecographic sign of recurrence.
DISCUSSION
Extrapleural SFTs are anatomically ubiquitous, as
Figure 1: Nodular, small solitary fibrous tumor of bladder mucosa.
Complete excision was performed (HE, ×10) documented also by the present case report, and
occur equally in males and females, primarily in adult
life, with a wide range of ages, 20 to 70 years. [4,5]
The ubiquity of SFT supports its mesenchymal origin
(with fibroblastic/myofibroblastic features). Most
[3]
present as a slow-growing, painless masses. In
cases of bladder SFT, the most frequent symptoms,
such as pain, palpable mass, abdominal distention,
urinary retention, haematuria, constipation, and bowel
obstruction, are related to compression and local
invasion of nearby structures.
In the English literature 15 cases have been
reported, [6,8-11] all with symptoms related to tumor
volume (up to 12 cm in diameter), and presence of
radiologic findings. [12-16] Sometimes, a diagnosis of
malignant soft tissue tumor was considered. Actual
[7]
Figure 2: Mesenchymal proliferation with low cellularity, without malignant bladder SFT has been described, while to
atypia, and without mitotic activity (HE, ×40) the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of a
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ September 30, 2016 389