Page 12 - Read Online
P. 12
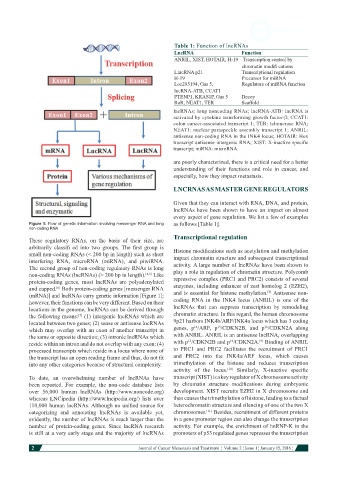
Table 1: Function of lncRNAs
LncRNA Function
ANRIL, XIST, HOTAIR, H-19 Transcription control by
chromatin modifi cations
LincRNA p21 Transcriptional regulation
H-19 Precursor for miRNA
Loc285194, Gas 5, Regulators of miRNA function
lncRNA-ATB, CCAT1
PTENP1, KRAS1P, Gas 5 Decoy
RoR, NEAT1, TER Scaffold
lncRNAs: long noncoding RNAs; lncRNA-ATB: lncRNA is
activated by cytokine transforming growth factor-β; CCAT1:
colon cancer-associated transcript 1; TER: telomerase RNA;
NEAT1: nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1; ANRIL:
antisense non-coding RNA in the INK4 locus; HOTAIR: Hox
transcript antisense intergenic RNA; XIST: X-inactive specific
transcript; miRNA: microRNA
are poorly characterized, there is a critical need for a better
understanding of their functions and role in cancer, and
especially, how they impact metastasis.
LNCRNAS AS MASTER GENE REGULATORS
Given that they can interact with RNA, DNA, and protein,
lncRNAs have been shown to have an impact on almost
every aspect of gene regulation. We list a few of examples
Figure 1: Flow of genetic information involving messenger RNA and long as follows [Table 1].
non-coding RNA
Transcriptional regulation
These regulatory RNAs, on the basis of their size, are
arbitrarily classifi ed into two groups. The first group is Histone modifications such as acetylation and methylation
small non-coding RNAs (< 200 bp in length) such as short impact chromatin structure and subsequent transcriptional
interfering RNA, microRNA (miRNA), and piwiRNA.
The second group of non-coding regulatory RNAs is long activity. A large number of lncRNAs have been shown to
non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) (> 200 bp in length). [4,5] Like play a role in regulation of chromatin structure. Polycomb
protein-coding genes, most lncRNAs are polyadenylated repressive complex (PRC1 and PRC2) consists of several
and capped. Both protein-coding genes [messenger RNA enzymes, including enhancer of zest homolog 2 (EZH2),
[6]
[8]
(mRNA)] and lncRNAs carry genetic information [Figure 1]; and is essential for histone methylation. Antisense non-
however, their functions can be very different. Based on their coding RNA in the INK4 locus (ANRIL) is one of the
locations in the genome, lncRNAs can be derived through lncRNAs that can suppress transcription by remodeling
the following means: (1) intergenic lncRNAs which are chromatin structure. In this regard, the human chromosome
[7]
located between two genes; (2) sense or antisense lncRNAs 9p21 harbors INK4b/ARF/INK4a locus which has 3 coding
16
15
14
which may overlap with an exon of another transcript in genes, p /ARF, p /CDKN2B, and p /CDKN2A along
the same or opposite direction; (3) intronic lncRNAs which with ANRIL. ANRIL is an antisense lncRNA, overlapping
16
[9]
15
reside within an intron and do not overlap with any exon; (4) with p /CDKN2B and p /CDKN2A. Binding of ANRIL
processed transcripts which reside in a locus where none of to PRC1 and PRC2 facilitates the recruitment of PRC1
the transcript has an open reading frame and thus, do not fit and PRC2 into the INK4a/ARF locus, which causes
into any other categories because of structural complexity. trimethylation of the histone and reduces transcription
activity of the locus. Similarly, X-inactive specific
[10]
To date, an overwhelming number of lncRNAs have transcript (XIST) is a key regulator of X chromosome activity
been reported. For example, the non-code database lists by chromatin structure modifications during embryonic
over 56,000 human lncRNAs (http://www.noncode.org) development. XIST recruits EZH2 in X chromosome and
whereas LNCipedia (http://www.lncipedia.org/) lists over then causes the trimethylation of histone, leading to a factual
110,000 human lncRNAs. Although no unified source for heterochromatin structure and silencing of one of the two X
categorizing and annotating lncRNAs is available yet, chromosomes. Besides, recruitment of different proteins
[11]
evidently, the number of lncRNAs is much larger than the in a gene promoter region can also change the transcription
number of protein-coding genes. Since lncRNA research activity. For example, the enrichment of hnRNP-K in the
is still at a very early stage and the majority of lncRNAs promoters of p53 regulated genes represses the transcription
2
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ Issue 1 ¦ January 15, 2016 ¦