Page 198 - Read Online
P. 198
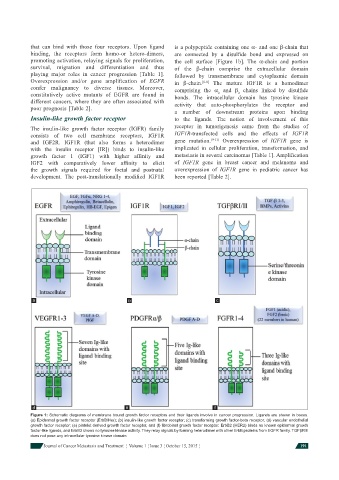
that can bind with those four receptors. Upon ligand is a polypeptide containing one α- and one β-chain that
binding, the receptors form homo-or hetero-dimers, are connected by a disulfi de bond and expressed on
promoting activation, relaying signals for proliferation, the cell surface [Figure 1b]. The α-chain and portion
survival, migration and differentiation and thus of the β-chain comprise the extracellular domain
playing major roles in cancer progression [Table 1]. followed by transmembrane and cytoplasmic domain
Overexpression and/or gene amplifi cation of EGFR in β-chain. [6-8] The mature IGF1R is a homodimer
confer malignancy to diverse tissues. Moreover, comprising the α and β chains linked by disulfi de
2
2
constitutively active mutants of EGFR are found in bonds. The intracellular domain has tyrosine kinase
different cancers, where they are often associated with activity that auto-phosphorylates the receptor and
poor prognosis [Table 2].
a number of downstream proteins upon binding
Insulin-like growth factor receptor to the ligands. The notion of involvement of this
The insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGFR) family receptor in tumorigenesis came from the studies of
consists of two cell membrane receptors, IGF1R IGF1R-transfected cells and the effects of IGF1R
and IGF2R. IGF1R (that also forms a heterodimer gene mutation. [9-11] Overexpression of IGF1R gene is
with the insulin receptor [IR]) binds to insulin-like implicated in cellular proliferation, transformation, and
growth factor 1 (IGF1) with higher affi nity and metastasis in several carcinomas [Table 1]. Amplifi cation
IGF2 with comparatively lower affi nity to elicit of IGF1R gene in breast cancer and melanoma and
the growth signals required for foetal and postnatal overexpression of IGF1R gene in pediatric cancer has
development. The post-translationally modifi ed IGF1R been reported [Table 2].
a b c
d e f
Figure 1: Schematic diagrams of membrane bound growth factor receptors and their ligands involve in cancer progression. Ligands are shown in boxes.
(a) Epidermal growth factor receptor (ErbB/Her); (b) insulin-like growth factor receptor; (c) transforming growth factor-beta receptor; (d) vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor; (e) platelet derived growth factor receptor, and (f) fi broblast growth factor receptor. ErbB2 (HER2) binds no known epidermal growth
factor-like ligands, and ErbB3 shows no tyrosine kinase activity. They relay signals by forming heterodimer with other ErbB proteins from EGFR family. TGFβRIII
does not pose any intracellular tyrosine kinase domain
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 1 ¦ Issue 3 ¦ October 15, 2015 ¦ 191