Page 81 - Read Online
P. 81
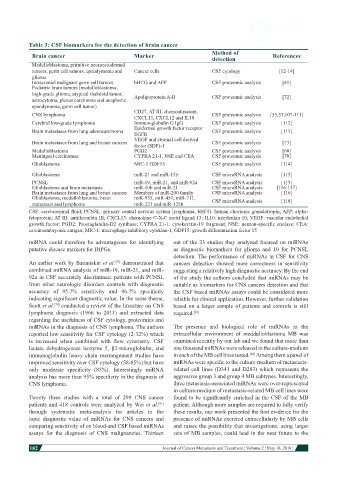
Table 3: CSF biomarkers for the detection of brain cancer
Method of
Brain cancer Marker detection References
Medulloblastoma, primitive neuroectodermal
tumors, germ cell tumors, ependymoma and Cancer cells CSF cytology [12-14]
glioma
Intracranial malignant germ cell tumors bHCG and AFP CSF proteomic analysis [41]
Pediatric brain tumors (medulloblastoma ,
high-grade glioma, atypical rhabdoid tumor, Apolipoprotein A-II CSF proteomic analysis [72]
astrocytoma, plexus carcinoma and anaplastic
ependymoma, germ cell tumor)
CNS lymphoma CD27, AT III, chemoattractant, CSF proteomic analysis [55,57,107-111]
CXCL13, CXCL12 and IL10
Cerebral low-grade lymphoma Immunoglobulin G IgG CSF proteomic analysis [112]
Brain metastases from lung adenocarcinoma Epidermal growth factor receptor CSF proteomic analysis [113]
EGFR
Brain metastases from lung and breast cancers VEGF and stromal cell derived CSF proteomic analysis [73]
factor (SDF)-1
Medulloblastoma PGD2 CSF proteomic analysis [60]
Meningeal carcinomas CYFRA 21-1, NSE and CEA CSF proteomic analysis [70]
Glioblastoma MIC-1 GDF15 CSF proteomic analysis [114]
Glioblastoma miR-21 and miR-15b CSF microRNA analysis [115]
PCNSL miR-19, miR-21, and miR-92a CSF microRNA analysis [115]
Glioblastoma and brain metastasis miR-10b and miR-21 CSF microRNA analysis [116-117]
Brain metastases from lung and breast cancers Members of miR-200 family CSF microRNA analysis [116]
Glioblastoma, medulloblastoma, brain miR-935, miR-451, miR-711, CSF microRNA analysis [118]
metastasis and lymphoma miR-223 and miR-125b
CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; PCNSL: primary central nervous system lymphoma; bHCG: human chorionic gonadotropin; AFP: alpha-
fetoprotein; AT III: antithrombin III; CXCL13: chemokine C-X-C motif ligand 13; IL10: interleukin 10; VEGF: vascular endothelial
growth factor; PGD2: Prostaglandin-D2 synthase; CYFRA 21-1: cytokeratin-19 fragment; NSE: neuron-specific enolase; CEA:
carcinoembryonic antigen; MIC-1: macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1; GDF15: growth differentiation factor 15
miRNA could therefore be advantageous for identifying out of the 23 studies they analyzed focused on miRNAs
putative disease markers for DIPGs. as diagnostic biomarkers for glioma and 10 for PCNSL
detection. The performance of miRNAs in CSF for CNS
An earlier work by Baraniskin et al. demonstrated that cancers detection showed more correctness in sensitivity
[77]
combined miRNA analysis of miR-19, miR-21, and miR- suggesting a relatively high diagnostic accuracy. By the end
92a in CSF accurately discriminate patients with PCNSL of the study the authors concluded that miRNAs may be
from other neurologic disorders controls with diagnostic suitable as biomarkers for CNS cancers detection and that
accuracy of 95.7% sensitivity and 96.7% specificity the CSF based miRNAs assays could be considered more
indicating significant diagnostic value. In the same theme, reliable for clinical application. However, further validation
Scott et al. conducted a review of the literature on CNS based on a larger sample of patients and controls is still
[79]
lymphoma diagnosis (1966 to 2011) and extracted data required. [81]
regarding the usefulness of CSF cytology, proteomics and
miRNAs in the diagnosis of CNS lymphoma. The authors The presence and biological role of miRNAs in the
reported low sensitivity for CSF cytology (2-32%) which extracellular environment of meddulloblastoma MB was
is increased when combined with flow cytometry. CSF examined recently by our lab and we found that more than
lactate dehydrogenase isozyme 5, β2-microglobulin, and one thousand miRNAs were released in the culture-medium
immunoglobulin heavy chain rearrangement studies have in each of the MB cell lines tested. Among them a panel of
[82]
improved sensitivity over CSF cytology (58-85%) but have miRNAs were specific to the culture-medium of metastasis-
only moderate specificity (85%). Interestingly miRNA related cell lines (D341 and D283) which represents the
analysis has more than 95% specificity in the diagnosis of aggressive group 3 and group 4 MB subtypes. Interestingly,
CNS lymphoma. three metastasis-associated miRNAs were over-represented
in culture-medium of metastasis-related MB cell lines were
Twenty three studies with a total of 299 CNS cancer found to be significantly enriched in the CSF of the MB
patients and 418 controls were analyzed by Wei et al. patient. Although more samples are required to fully verify
[81]
through systematic meta-analysis for articles in the these results, our work presented the first evidence for the
topic diagnostic value of miRNAs for CNS cancers and presence of miRNAs excreted extracellularly by MB cells
comparing sensitivity of on blood-and CSF based miRNAs and raises the possibility that investigations, using larger
assays for the diagnosis of CNS malignancies. Thirteen sets of MB samples, could lead in the near future to the
182
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ May 18, 2016 ¦