Page 72 - Read Online
P. 72
Yonemura et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2022;8:43 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2022.49 Page 5 of 12
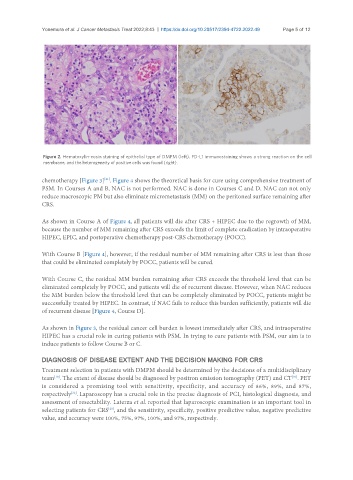
Figure 2. Hematoxylin-eosin staining of epithelial type of DMPM (left). PD-L1 immunostaining shows a strong reaction on the cell
membrane, and the heterogeneity of positive cells was found (right).
chemotherapy [Figure 3] . Figure 4 shows the theoretical basis for cure using comprehensive treatment of
[21]
PSM. In Courses A and B, NAC is not performed. NAC is done in Courses C and D. NAC can not only
reduce macroscopic PM but also eliminate micrometastasis (MM) on the peritoneal surface remaining after
CRS.
As shown in Course A of Figure 4, all patients will die after CRS + HIPEC due to the regrowth of MM,
because the number of MM remaining after CRS exceeds the limit of complete eradication by intraoperative
HIPEC, EPIC, and postoperative chemotherapy post-CRS chemotherapy (POCC).
With Course B [Figure 4], however, if the residual number of MM remaining after CRS is less than those
that could be eliminated completely by POCC, patients will be cured.
With Course C, the residual MM burden remaining after CRS exceeds the threshold level that can be
eliminated completely by POCC, and patients will die of recurrent disease. However, when NAC reduces
the MM burden below the threshold level that can be completely eliminated by POCC, patients might be
successfully treated by HIPEC. In contrast, if NAC fails to reduce this burden sufficiently, patients will die
of recurrent disease [Figure 4, Course D].
As shown in Figure 3, the residual cancer cell burden is lowest immediately after CRS, and intraoperative
HIPEC has a crucial role in curing patients with PSM. In trying to cure patients with PSM, our aim is to
induce patients to follow Course B or C.
DIAGNOSIS OF DISEASE EXTENT AND THE DECISION MAKING FOR CRS
Treatment selection in patients with DMPM should be determined by the decisions of a multidisciplinary
[10]
[10]
team . The extent of disease should be diagnosed by positron emission tomography (PET) and CT . PET
is considered a promising tool with sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 86%, 89%, and 87%,
[22]
respectively . Laparoscopy has a crucial role in the precise diagnosis of PCI, histological diagnosis, and
assessment of resectability. Laterza et al. reported that laparoscopic examination is an important tool in
selecting patients for CRS , and the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive
[23]
value, and accuracy were 100%, 75%, 97%, 100%, and 97%, respectively.