Page 10 - Read Online
P. 10
Fitzgerald et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:54 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.97 Page 5 of 11
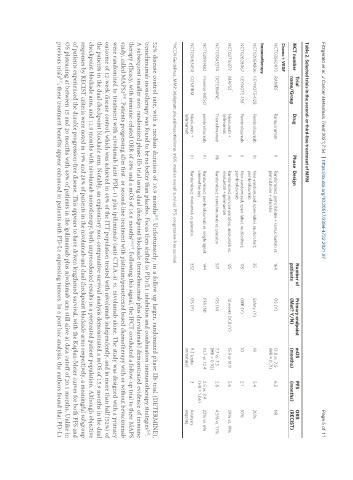
Table 2. Selected trials in the second- or third-line treatment of MPM
Trial Number of Primary endpoint mOS PFS ORR
NCT number Drug Phase Design
name/Group patients (Met? Y/N) (months) (months) (RECIST)
Chemo + VEGF
NCT03560973 RAMES Ramucirumab II Randomized, gemcitabine + ramucirumab vs. 164 OS (Y) 13.8 vs. 7.5 6.2 NR
gemcitabine + placebo (HR = 0.71)
Immunotherapy
NCT02054806 KEYNOTE-028 Pembrolizumab Ib Non-randomized, open-label, multicohort; 35 Safety (Y) 18 5.4 20%
pembrolizumab
*
NCT02628067 KEYNOTE-158 Pembrolizumab II Non-randomized, open-label, multicohort; 118 ORR (Y) 10 2.1 10%
pembrolizumab
*
NCT02716272 MAPS2 Nivolumab + II Randomized, noncomparative; nivolumab vs. 125 12 weeks DCR (Y) 15.9 or 11.9 5.6 29% vs. 19%
Ipilimumab nivolumab + ipilimumab
NCT01843374 DETERMINE Tremelimumab IIb Randomized; tremelimumab vs. placebo 571 OS (N) 7.7 vs. 7.3 2.8 4.5% vs. 1.1%
(HR = 0.92)
NCT02991482 Promise-MESO pembrolizumab III Randomized; pembrolizumab vs. single agent 144 PFS (N) 10.7 vs. 12.4 2.5 vs. 3.4 22% vs. 6%
chemotherapy (HR = 1.06)
NCT03063450 CONFIRM Nivolumab + III Randomized; nivolumab vs. placebo 332 OS (Y) 9.2 (data 3 Analysis
Ipilimumab immature) ongoing
*NCCN Guidelines. MMP: Malignant pleural mesothelioma; mOS: median overall survival; PFS: progression-free survival.
[15]
52% disease control rate, with a median duration of 10.9 months . Unfortunately, in a follow up larger, randomized phase IIb trial (DETERMINE),
tremelimumab monotherapy was found to be no better than placebo. Focus then shifted to PD1/L1 inhibition and combination immunotherapy strategies .
[16]
A subsequent smaller non-randomized phase IIb trial using dual checkpoint blockade (tremelimumab plus durvalumab) demonstrated evidence of immune
therapy efficacy, with immune-related ORR of 28% and a mOS of 16.6 months [16,17] . Following this signal, the IFCT conducted a follow-up trial to their MAPS
study, called MAPS2 . Patients progressing after first- or second-line treatment with platinum/pemetrexed based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab
[18]
were randomized to treatment with nivolumab (anti PDL-1) plus ipilimumab (anti CTLA-4) vs. nivolumab alone. The study was designed with a primary
outcome of 12-week disease control, which was achieved in 40% of the ITT population treated with nivolumab independently, and in more than half (52%) of
the patients in the dual checkpoint blockade arm. Notably, an exploratory non-comparative survival analysis demonstrated a mOS of 15.9 months in the dual
checkpoint blockade arm, and 11.9 months with nivolumab monotherapy, both unprecedented results in a pretreated patient population. Although objective
responses by RECIST criteria were noted in 19% and 28% of patients in the nivolumab and dual checkpoint blockade arms respectively, a meaningful subgroup
of patients experienced the durable progression-free disease. This appears to have driven lengthened survival, with the Kaplan-Meier curves for both PFS and
OS plateauing at between 15 and 20 months with 48% of patients in the ipilimumab plus nivolumab arm still alive at data cutoff of 20.1 months. Unlike in
[17]
previous trials , these treatment benefits appear enhanced in patients with PD-L1 expressing tumors. In a post hoc analysis, the authors found that PD-L1