Page 37 - Read Online
P. 37
CSC markers, including CD133, CD44, CD24, In addition to cell surface markers, activities of certain
CD166, Lgr-5, and aldehyde dehydrogenase pathways or enzymes may also act as markers of
1 (ALDH1) [Table 1]. [26] CD133, a pentaspan stemness. For instance, normal colorectal stem cells can
transmembrane glycoprotein, [27] was one of the fi rst be identifi ed by the activity of ALDH1, a detoxifying
colorectal CSC markers to be identifi ed. [19,20] However, enzyme that oxidizes intracellular aldehydes. [35,36]
although selecting CRC cells based on AC133 ALDH1+ cells were sparse and restricted to the bottom of
positivity, an epitope of the CD133 protein identifi es normal crypts, where stem cells reside but were increased
the tumorigenic and clonogenic population. [28] CD133 in number and distributed further up the crypts during
expression has been detected throughout the normal progression from normal epithelium to adenoma. In
[37]
gastrointestinal tract and is not restricted to the stem addition, implantation of ALDH1+ colon cancer cells into
cell compartment. [29,30] In addition, both CD133+ and NOD/SCID mice generated xenograft tumors, whereas
CD133- metastatic CRC cells were able to form new ALDH1- cells did not. These fi ndings indicate that
[37]
tumors, suggesting that CD133 may not be a reliable ALDH1 activity may be a useful colorectal CSC marker.
marker of CSCs. [29]
Other markers include CD166, epithelial cell adhesion
The cell adhesion molecule CD44 has been identifi ed molecule, CD29, CD24, CD26, Msi-1, Lgr-5, and Wnt
as a cell surface marker associated with CSCs in activity/β-catenin. [38-42] The presence of these molecules
[31]
several types of tumor. CD44+ cells exhibited has been associated with stemness characteristics both
CSC properties, and a single cell could form a sphere in vitro and in vivo. These markers were also used to
in vitro, and a xenograft tumor resembling the original enrich isolated CSCs further to enhance their tumorigenic
[32]
lesion in vitro. Overexpression of CD44 in CRC has ability. The transcription factors Oct-4 and Sox2 are
been associated with depth of invasion and lymph node also promising CSC markers, given their roles in cell
involvement and is shown to be an independent predictor renewal. Oct-4 and Sox2 levels have been shown to be
of overall survival. Although CD44, like CD133, is elevated in CRC and to correlate with increased CSC
[33]
not a specifi c marker for colorectal CSCs, it is possible proliferation and poor prognosis. [43,44] Other pluripotency
that a combination of these two markers may be more genes, Nanog, Lin-28, Klf-4, and c-myc, are regarded as
reliable for detecting colorectal CSCs than either marker promising surrogate markers, given that they appear to
alone. [34] facilitate a shift towards an undifferentiated state. [45]
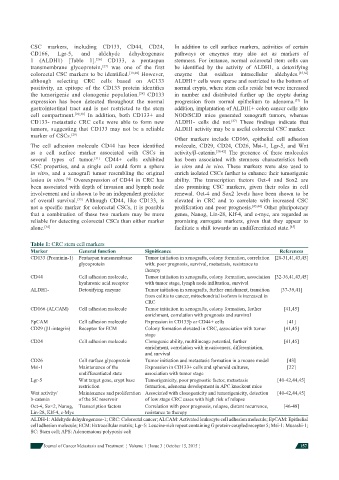
Table 1: CRC stem cell markers
Marker General function Signifi cance References
CD133 (Prominin-1) Pentaspan transmembrane Tumor initiation in xenografts, colony formation, correlation [28-31,41,43,45]
glycoprotein with: poor prognosis, survival, metastasis, resistance to
therapy
CD44 Cell adhesion molecule, Tumor initiation in xenografts, colony formation, association [32-36,41,43,45]
hyaluronic acid receptor with tumor stage, lymph node infi ltration, survival
ALDH1- Detoxifying enzyme Tumor initiation in xenografts, further enrichment, transition [37-39,41]
from colitis to cancer, mitochondrial isoform is increased in
CRC
CD166 (ALCAM) Cell adhesion molecule Tumor initiation in xenografts, colony formation, further [41,45]
enrichment, correlation with prognosis and survival
EpCAM Cell adhesion molecule Expression in CD133þ or CD44+ cells [41]
CD29 (β1-integrin) Receptor for ECM Colony formation elevated in CRC, association with tumor [41,45]
stage
CD24 Cell adhesion molecule Clonogenic ability, multilineage potential, further [41,45]
enrichment, correlation with invasiveness, differentiation,
and survival
CD26 Cell surface glycoprotein Tumor initiation and metastasis formation in a mouse model [43]
Msi-1 Maintenance of the Expression in CD133+ cells and spheroid cultures, [22]
undifferentiated state association with tumor stage
Lgr-5 Wnt target gene, crypt base Tumorigenicity, poor prognostic factor, metastasis [40-42,44,45]
restriction formation, adenoma development in APC knockout mice
Wnt activity/ Maintenance and proliferation Associated with clonogenicity and tumorigenicity, detection [40-42,44,45]
b-catenin of the SC reservoir of low stage CRC cases with high risk of relapse
Oct-4, So×2, Nanog, Transcription factors Correlation with poor prognosis, relapse, distant recurrence, [46-48]
Lin-28, Klf-4, c-Myc resistance to therapy
ALDH-1: Aldehyde dehydrogenase-1; CRC: Colorectal cancer; ALCAM: Activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule; EpCAM: Epithelial
cell adhesion molecule; ECM: Extracellular matrix; Lgr-5: Leucine-rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 5; Msi-1: Musashi-1;
SC: Stem cell; APS: Adenomatous polyposis coli
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 1 ¦ Issue 3 ¦ October 15, 2015 ¦ 157