Page 56 - Read Online
P. 56
Page 4 of 11 Tirelli et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2023;9:20 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2022.98
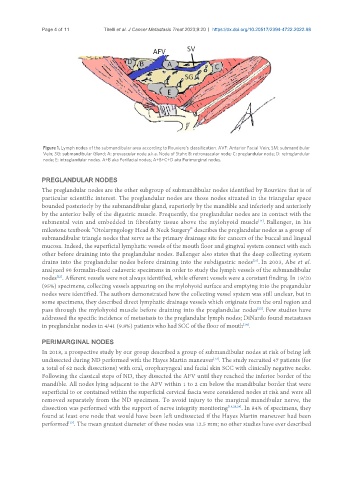
Figure 1. Lymph nodes of the submandibular area according to Rouviere’s classification. AVF: Anterior Facial Vein; SM: submandibular
Vein; SG: submandibular Gland; A: prevascular node a.k.a. Node of Stahr; B: retrovascular node; C: preglandular node; D: retroglandular
node; E: intraglandular nodes. A+B aka Perifacial nodes; A+B+C+D aka Perimarginal nodes.
PREGLANDULAR NODES
The preglandular nodes are the other subgroup of submandibular nodes identified by Rouvière that is of
particular scientific interest. The preglandular nodes are those nodes situated in the triangular space
bounded posteriorly by the submandibular gland, superiorly by the mandible and inferiorly and anteriorly
by the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. Frequently, the preglandular nodes are in contact with the
submental vein and embedded in fibrofatty tissue above the mylohyoid muscle . Ballenger, in his
[14]
milestone textbook “Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery” describes the preglandular nodes as a group of
submandibular triangle nodes that serve as the primary drainage site for cancers of the buccal and lingual
mucosa. Indeed, the superficial lymphatic vessels of the mouth floor and gingival system connect with each
other before draining into the preglandular nodes. Ballenger also states that the deep collecting system
drains into the preglandular nodes before draining into the subdigastric nodes . In 2003, Abe et al.
[21]
analyzed 90 formalin-fixed cadaveric specimens in order to study the lymph vessels of the submandibular
nodes . Afferent vessels were not always identified, while efferent vessels were a constant finding. In 19/20
[22]
(95%) specimens, collecting vessels appearing on the mylohyoid surface and emptying into the pregandular
nodes were identified. The authors demonstrated how the collecting vessel system was still unclear, but in
some specimens, they described direct lymphatic drainage vessels which originate from the oral region and
pass through the mylohyoid muscle before draining into the preglandular nodes . Few studies have
[22]
addressed the specific incidence of metastasis to the preglandular lymph nodes; DiNardo found metastases
in preglandular nodes in 4/41 (9.8%) patients who had SCC of the floor of mouth .
[14]
PERIMARGINAL NODES
In 2018, a prospective study by our group described a group of submandibular nodes at risk of being left
undissected during ND performed with the Hayes Martin maneuver . The study recruited 47 patients (for
[13]
a total of 62 neck dissections) with oral, oropharyngeal and facial skin SCC with clinically negative necks.
Following the classical steps of ND, they dissected the AFV until they reached the inferior border of the
mandible. All nodes lying adjacent to the AFV within 1 to 2 cm below the mandibular border that were
superficial to or contained within the superficial cervical fascia were considered nodes at risk and were all
removed separately from the ND specimen. To avoid injury to the marginal mandibular nerve, the
dissection was performed with the support of nerve integrity monitoring [13,23,24] . In 84% of specimens, they
found at least one node that would have been left undissected if the Hayes Martin maneuver had been
[13]
performed . The mean greatest diameter of these nodes was 12.5 mm; no other studies have ever described