Page 20 - Read Online
P. 20
Page 4 of 8 Dankbaar et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:56 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.112
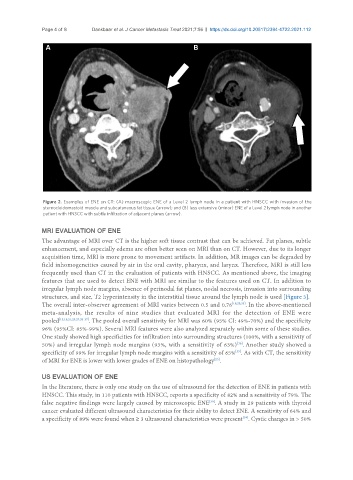
Figure 2. Examples of ENE on CT: (A) macroscopic ENE of a Level 2 lymph node in a patient with HNSCC with invasion of the
sternocleidomastoid muscle and subcutaneous fat tissue (arrow); and (B) less extensive (minor) ENE of a Level 2 lymph node in another
patient with HNSCC with subtle infiltration of adjacent planes (arrow).
MRI EVALUATION OF ENE
The advantage of MRI over CT is the higher soft tissue contrast that can be achieved. Fat planes, subtle
enhancement, and especially edema are often better seen on MRI than on CT. However, due to its longer
acquisition time, MRI is more prone to movement artifacts. In addition, MR images can be degraded by
field inhomogeneities caused by air in the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx. Therefore, MRI is still less
frequently used than CT in the evaluation of patients with HNSCC. As mentioned above, the imaging
features that are used to detect ENE with MRI are similar to the features used on CT. In addition to
irregular lymph node margins, absence of perinodal fat planes, nodal necrosis, invasion into surrounding
structures, and size, T2 hyperintensity in the interstitial tissue around the lymph node is used [Figure 3].
The overall inter-observer agreement of MRI varies between 0.5 and 0.76 [18,25,33] . In the above-mentioned
meta-analysis, the results of nine studies that evaluated MRI for the detection of ENE were
pooled [15,18,21,25,27,33-37] . The pooled overall sensitivity for MRI was 60% (95% CI: 49%-70%) and the specificity
96% (95%CI: 85%-99%). Several MRI features were also analyzed separately within some of these studies.
One study showed high specificities for infiltration into surrounding structures (100%, with a sensitivity of
[36]
50%) and irregular lymph node margins (93%, with a sensitivity of 63%) . Another study showed a
specificity of 99% for irregular lymph node margins with a sensitivity of 65% . As with CT, the sensitivity
[35]
of MRI for ENE is lower with lower grades of ENE on histopathology .
[25]
US EVALUATION OF ENE
In the literature, there is only one study on the use of ultrasound for the detection of ENE in patients with
HNSCC. This study, in 110 patients with HNSCC, reports a specificity of 82% and a sensitivity of 79%. The
false negative findings were largely caused by microscopic ENE . A study in 29 patients with thyroid
[38]
cancer evaluated different ultrasound characteristics for their ability to detect ENE. A sensitivity of 64% and
a specificity of 89% were found when ≥ 3 ultrasound characteristics were present . Cystic changes in > 50%
[39]