Page 40 - Read Online
P. 40
Matrone et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:23 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.47 Page 7 of 19
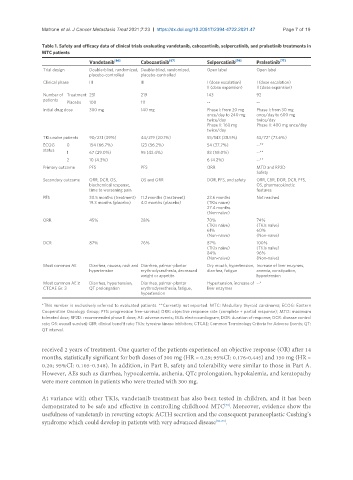
Table 1. Safety and efficacy data of clinical trials evaluating vandetanib, cabozantinib, selpercatinib, and pralsetinib treatments in
MTC patients
Vandetanib [66] Cabozantinib [67] Selpercatinib [76] Pralsetinib [77]
Trial design Double-blind, randomized, Double-blind, randomized, Open label Open label
placebo-controlled placebo-controlled
Clinical phase III III I (dose escalation) I (dose escalation)
II (dose expansion) II (dose expansion)
Number of Treatment 231 219 143 92
patients
Placebo 100 111 -- --
Initial drug dose 300 mg 140 mg Phase I: from 20 mg Phase I: from 30 mg
once/day to 240 mg once/day to 600 mg
twice/day twice/day
Phase II: 160 mg Phase II: 400 mg once/day
twice/day
TKIs naïve patients 90/231 (39%) 44/219 (20.1%) 55/143 (38.5%) 53/72* (73.6%)
ECOG 0 154 (66.7%) 123 (56.2%) 54 (37.7%) --**
status
1 67 (29.0%) 95 (43.4%) 83 (58.0%) --**
2 10 (4.3%) 6 (4.2%) --**
Primary outcome PFS PFS ORR MTD and RP2D
Safety
Secondary outcome ORR, DCR, OS, OS and ORR DOR, PFS, and safety ORR, CBR, DOR, DCR, PFS,
biochemical response, OS, pharmacokinetic
time to worsening pain features
PFS 30.5 months (treatment) 11.2 months (treatment) 23.6 months Not reached
19.3 months (placebo) 4.0 months (placebo) (TKIs naïve)
27.4 months
(Non-naïve)
ORR 45% 28% 70% 74%
(TKIs naïve) (TKIs naïve)
61% 60%
(Non-naïve) (Non-naïve)
DCR 87% 76% 87% 100%
(TKIs naïve) (TKIs naïve)
84% 96%
(Non-naïve) (Non-naïve)
Most common AE Diarrhea, nausea, rash and Diarrhea, palmar-plantar Dry mouth, hypertension, Increase of liver enzymes,
hypertension erythrodysesthesia, decreased diarrhea, fatigue anemia, constipation,
weight or appetite hypertension
Most common AE ≥ Diarrhea, hypertension, Diarrhea, palmar-plantar Hypertension, increase of --*
CTCAE Gr. 3 QT prolongation erythrodysesthesia, fatigue, liver enzymes
hypertension
*This number is exclusively referred to evaluated patients. **Currently not reported. MTC: Medullary thyroid carcinoma; ECOG: Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group; PFS: progression free-survival; ORR: objective response rate (complete + partial response); MTD: maximum
tolerated dose; RP2D: recommended phase II dose; AE: adverse events; EKG: electrocardiogram; DOR: duration of response; DCR: disease control
rate; OS: overall survival; CBR: clinical benefit rate; TKIs: tyrosine kinase inhibitors; CTCAE: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; QT:
QT interval.
received 2 years of treatment. One quarter of the patients experienced an objective response (OR) after 14
months, statistically significant for both doses of 300 mg (HR = 0.29; 95%CI: 0.176-0.445) and 150 mg (HR =
0.20; 95%CI: 0.105-0.348). In addition, in Part B, safety and tolerability were similar to those in Part A.
However, AEs such as diarrhea, hypocalcemia, asthenia, QTc prolongation, hypokalemia, and keratopathy
were more common in patients who were treated with 300 mg.
At variance with other TKIs, vandetanib treatment has also been tested in children, and it has been
demonstrated to be safe and effective in controlling childhood MTC . Moreover, evidence show the
[79]
usefulness of vandetanib in reverting ectopic ACTH secretion and the consequent paraneoplastic Cushing’s
syndrome which could develop in patients with very advanced disease [80-83] .