Page 37 - Read Online
P. 37
Page 4 of 19 Matrone et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:23 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.47
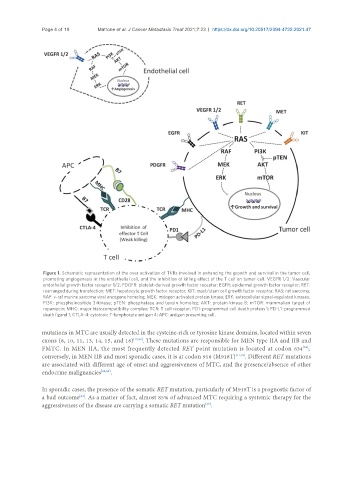
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the over activation of TKRs involved in enhancing the growth and survival in the tumor cell,
promoting angiogenesis in the endothelial cell, and the inhibition of killing effect of the T cell on tumor cell. VEGFR 1/2: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 1/2; PDGFR: platelet-derived growth factor receptor; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; RET:
rearranged during transfection; MET: hepatocyte growth factor receptor; KIT: mast/stem cell growth factor receptor; RAS: rat sarcoma;
RAF: v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; MEK: mitogen activated protein kinase; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinases;
PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; pTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog; AKT: protein kinase B; mTOR: mammalian target of
rapamycin; MHC: major histocompatibility complex; TCR: T cell receptor; PD1: programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1: programmed
death ligand 1; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4; APC: antigen presenting cell.
mutations in MTC are usually detected in the cysteine-rich or tyrosine kinase domains, located within seven
exons (8, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15, and 16) [19,52] . These mutations are responsible for MEN type IIA and IIB and
FMTC. In MEN IIA, the most frequently detected RET point mutation is located at codon 634 ;
[53]
conversely, in MEN IIB and most sporadic cases, it is at codon 918 (M918T) [11,15] . Different RET mutations
are associated with different age of onset and aggressiveness of MTC, and the presence/absence of other
endocrine malignancies [35,54] .
In sporadic cases, the presence of the somatic RET mutation, particularly of M918T is a prognostic factor of
a bad outcome . As a matter of fact, almost 85% of advanced MTC requiring a systemic therapy for the
[21]
aggressiveness of the disease are carrying a somatic RET mutation .
[55]