Page 110 - Read Online
P. 110
Spencer et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2022;8:2 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.174 Page 9 of 15
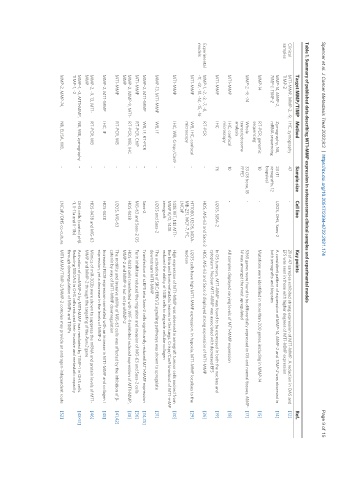
Table 1. Summary of published data describing MT1-MMP expression in osteosarcoma clinical samples and experimental models
Target MMP/TIMP Method Sample size Cell line Key points Ref.
Clinical MT1-MMP, MMP-2, -9, IHC, zymography 47 - 21 of 47 samples exhibited strong expression of MT1-MMP. A reduction in OAS and [12]
samples TIMP-2 EFS was seen in those with higher degrees of MT1-MMP expression
MMP-14, MMP-2, Zymography, NB, 23 (11 U2OS, OHS, Saos-2 A consistent pattern of expression of MMP-14, MMP-2 and TIMP-2 was observed in [14]
TIMP-1, TIMP-2 mRNA sequencing xenografts, 12 both xenografts and biopsies
biopsies)
MMP-14 RT-PCR, genomic 10 - Mutations were identified in more than 200 genes, including in MMP-14 [15]
sequencing
MMP-2, -9, -14 Whole 33 (18 bone, 15 - 5365 genes were found to be differentially expressed in OS and normal tissues. MMP- [17]
transcriptosome FFPE) 14 was amongst the most upregulated
analysis
MT1-MMP IHC, confocal 10 - All samples displayed varying levels of MT1-MMP expression [18]
microscopy
MT1-MMP IHC 76 U2OS, SJSA-2 In OS tumours, MT1-MMP was found to be expressed in both the nucleus and [19]
cytoplasm. Nuclear MT1-MMP was associated with decreased EFS
Experimental MMP-1, -2, -3, -7, -8, RT-PCR - HOS, MG-63 and Saos-2 HOS, MG-63 and Saos-2 displayed strong expression of MT1-MMP [26]
models -11, -12, -13, -14, -15, -16
MT1-MMP WB, IHC, confocal - HT1080, U2OS, MDA- U2OS cells have high MT1-MMP expression. In hypoxia, MT1-MMP localises to the [29]
microscopy MB-231, MCF-7, PC, nucleus
LNCaP
MT1-MMP IHC, WB, Crispr/Cas9 - 143B WT, 143 MT1- High expression of MT1-MMP was observed in xenograft tumour cells excised from [30]
MMP K/O, 143B the tibia and from metastatic lesions in the lungs. Crispr/Cas9 knockout of MT1-mMP
xenograft reduced the ability of 143B cells to degrade cellular collagen
MMP-13, MT1-MMP WB, IF - U2OS and Saos-2 The activation of SRC/ERK1/2 signalling pathways was shown to upregulate [31]
downstream MT1-MMP
MMP-2, MT1-MMP WB, IF, RT-PCR - Saos-2 Transfection of sLRP5 into Saos-2 cells significantly reduced MT1-MMP expression [34,35]
MT1-MMP RT-PCR, ChIP - MG-63 and Saos-2 OS Furin inhibition reduced the migration and invasion of MG-63 and Saos-2 cells [36]
MMP-2, MMP-9, MT1- RT-PCR, WB, IHC - HOS-143B HOS-143B cells transfected with WIF-1 exhibited reduced expression of MT1-MMP, [38]
MMP MMP-2 and MMP-9 but not proMMP-2
MT1-MMP RT-PCR, WB - U2OS, MG-63 The motility and invasive ability of MG-63 cells was affected by the inhibition of β- [41,42]
catenin by way of MT1-MMP downregulation
MMP-2, MT1-MMP IHC, IF - HOS-143B Increased PEDF expression correlated with an increase in MT1-MMP and collagen I [45]
expression, yet a decrease in the levels of MMP-2
MMP-2, -9, 13, MT1- RT-PCR, WB - HOS-143B and MG-63 Mimics of miR-302b were shown to suppress the mRNA and protein levels of MT1- [46]
MMP MMP and MMP-2 through the targeting of the Runx2 gene
MMP-1, -2, MT1-MMP, NB, WB, zymography - OHS cells (control pHβ Activation of proMMP-2 by MT1-MMP was mediated by TIMP-1 in OHS cells. [48-51]
TIMP-1, -2 -1, II-11a and II-11b) Reducing S100A4 in OHS cells reduced their invasive and metastatic capacity
through downregulation of MMPs and TIMPs
MMP-2, MMP-14, NB, ELISA, WB, - LNCaP/OHS co-culture MT1-MMP/TIMP-2/MMP-2 complex may provide an androgen-independent route [52]