Page 107 - Read Online
P. 107
Page 6 of 15 Spencer et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2022;8:2 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.174
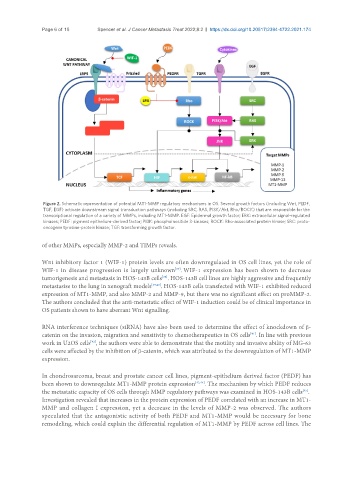
Figure 2. Schematic representation of potential MT1-MMP regulatory mechanisms in OS. Several growth factors (including Wnt, PEDF,
TGF, EGF) activate downstream signal transduction pathways (including SRC, RAS, PI3K/Akt, Rho/ROCK) that are responsible for the
transcriptional regulation of a variety of MMPs, including MT1-MMP. EGF: Epidermal growth factor; ERK: extracellular signal-regulated
kinases; PEDF: pigment epithelium-derived factor; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinases; ROCK: Rho-associated protein kinase; SRC: proto-
oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase; TGF: transforming growth factor.
of other MMPs, especially MMP-2 and TIMPs reveals.
Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF-1) protein levels are often downregulated in OS cell lines, yet the role of
WIF-1 in disease progression is largely unknown . WIF-1 expression has been shown to decrease
[37]
tumorigenesis and metastasis in HOS-143B cells . HOS-143B cell lines are highly aggressive and frequently
[38]
metastasise to the lung in xenograft models [39,40] . HOS-143B cells transfected with WIF-1 exhibited reduced
expression of MT1-MMP, and also MMP-2 and MMP-9, but there was no significant effect on proMMP-2.
The authors concluded that the anti-metastatic effect of WIF-1 induction could be of clinical importance in
OS patients shown to have aberrant Wnt signalling.
RNA interference techniques (siRNA) have also been used to determine the effect of knockdown of β-
catenin on the invasion, migration and sensitivity to chemotherapeutics in OS cells . In line with previous
[41]
work in U2OS cells , the authors were able to demonstrate that the motility and invasive ability of MG-63
[42]
cells were affected by the inhibition of β-catenin, which was attributed to the downregulation of MT1-MMP
expression.
In chondrosarcoma, breast and prostate cancer cell lines, pigment-epithelium derived factor (PEDF) has
been shown to downregulate MT1-MMP protein expression [43,44] . The mechanism by which PEDF reduces
the metastatic capacity of OS cells through MMP regulatory pathways was examined in HOS-143B cells .
[45]
Investigation revealed that increases in the protein expression of PEDF correlated with an increase in MT1-
MMP and collagen I expression, yet a decrease in the levels of MMP-2 was observed. The authors
speculated that the antagonistic activity of both PEDF and MT1-MMP would be necessary for bone
remodeling, which could explain the differential regulation of MT1-MMP by PEDF across cell lines. The