Page 81 - Read Online
P. 81
Grynkiewicz. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:48 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.112 Page 7 of 10
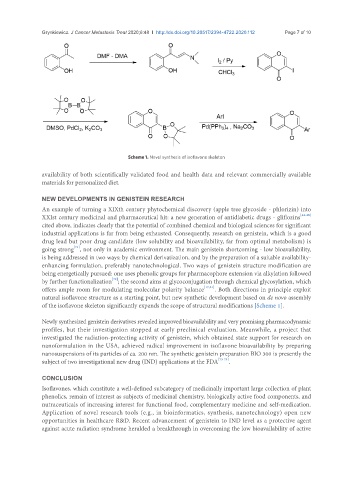
Scheme 1. Novel synthesis of isoflavone skeleton
availability of both scientifically validated food and health data and relevant commercially available
materials for personalized diet.
NEW DEVELOPMENTS IN GENISTEIN RESEARCH
An example of turning a XIXth century phytochemical discovery (apple tree glycoside - phlorizin) into
XXIst century medicinal and pharmaceutical hit: a new generation of antidiabetic drugs - gliflozins [44-46]
cited above, indicates clearly that the potential of combined chemical and biological sciences for significant
industrial applications is far from being exhausted. Consequently, research on genistein, which is a good
drug lead but poor drug candidate (low solubility and bioavailability, far from optimal metabolism) is
[71]
going strong , not only in academic environment. The main genistein shortcoming - low bioavailability,
is being addressed in two ways: by chemical derivatization, and by the preparation of a suitable availability-
enhancing formulation, preferably nanotechnological. Two ways of genistein structure modification are
being energetically pursued: one uses phenolic groups for pharmacophore extension via alkylation followed
[72]
by further functionalization ; the second aims at glycoconjugation through chemical glycosylation, which
offers ample room for modulating molecular polarity balance [17,21] . Both directions in principle exploit
natural isoflavone structure as a starting point, but new synthetic development based on de novo assembly
of the isoflavone skeleton significantly expands the scope of structural modifications [Scheme 1].
Newly synthesized genistein derivatives revealed improved bioavailability and very promising pharmacodynamic
profiles, but their investigation stopped at early preclinical evaluation. Meanwhile, a project that
investigated the radiation-protecting activity of genistein, which obtained state support for research on
nanoformulation in the USA, achieved radical improvement in isoflavone bioavailability by preparing
nanosuspensions of its particles of ca. 200 nm. The synthetic genistein preparation BIO 300 is presently the
subject of two investigational new drug (IND) applications at the FDA [73-75] .
CONCLUSION
Isoflavones, which constitute a well-defined subcategory of medicinally important large collection of plant
phenolics, remain of interest as subjects of medicinal chemistry, biologically active food components, and
nutraceuticals of increasing interest for functional food, complementary medicine and self-medication.
Application of novel research tools (e.g., in bioinformatics, synthesis, nanotechnology) open new
opportunities in healthcare R&D. Recent advancement of genistein to IND level as a protective agent
against acute radiation syndrome heralded a breakthrough in overcoming the low bioavailability of active