Page 27 - Read Online
P. 27
Pellerino et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:41 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.80 Page 9 of 20
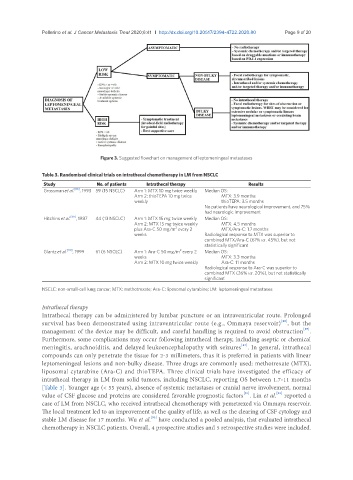
Figure 3. Suggested flowchart on management of leptomeningeal metastases
Table 3. Randomised clinical trials on intrathecal chemotherapy in LM from NSCLC
Study No. of patients Intrathecal therapy Results
Grossman et al. [88] , 1993 59 (15 NSCLC) Arm 1: MTX 10 mg twice weekly Median OS:
Arm 2: thioTEPA 10 mg twice MTX: 3.9 months
weekly thioTEPA: 3.5 months
No patients have neurological improvement, and 75%
had neurologic improvement
Hitchins et al. [89] , 1987 44 (13 NSCLC) Arm 1: MTX 15 mg twice weekly Median OS:
Arm 2: MTX 15 mg twice weekly MTX: 4.5 months
2
plus Ara-C 50 mg/m every 2 MTX/Ara-C: 1.7 months
weeks Radiological response to MTX was superior to
combined MTX/Ara-C (61% vs. 45%), but not
statistically significant
2
Glantz et al. [90] , 1999 61 (6 NSCLC) Arm 1: Ara-C 50 mg/m every 2 Median OS:
weeks MTX: 3.3 months
Arm 2: MTX 10 mg twice weekly Ara-C: 11 months
Radiological response to Ara-C was superior to
combined MTX (26% vs. 20%), but not statistically
significant
NSCLC: non-small-cell lung cancer; MTX: methotrexate; Ara-C: liposomal cytarabine; LM: leptomeningeal metastases
Intrathecal therapy
Intrathecal therapy can be administered by lumbar puncture or an intraventricular route. Prolonged
[86]
survival has been demonstrated using intraventricular route (e.g., Ommaya reservoir) , but the
[87]
management of the device may be difficult, and careful handling is required to avoid obstruction .
Furthermore, some complications may occur following intrathecal therapy, including aseptic or chemical
[87]
meningitis, arachnoiditis, and delayed leukoencephalopathy with seizures . In general, intrathecal
compounds can only penetrate the tissue for 2-3 millimeters, thus it is preferred in patients with linear
leptomeningeal lesions and non-bulky disease. Three drugs are commonly used: methotrexate (MTX),
liposomal cytarabine (Ara-C) and thioTEPA. Three clinical trials have investigated the efficacy of
intrathecal therapy in LM from solid tumors, including NSCLC, reporting OS between 1.7-11 months
[Table 3]. Younger age (< 55 years), absence of systemic metastases or cranial nerve involvement, normal
[91]
[92]
value of CSF glucose and proteins are considered favorable prognostic factors . Lin et al. reported a
case of LM from NSCLC, who received intrathecal chemotherapy with pemetrexed via Ommaya reservoir.
The local treatment led to an improvement of the quality of life, as well as the clearing of CSF cytology and
stable LM disease for 17 months. Wu et al. have conducted a pooled analysis, that evaluated intrathecal
[93]
chemotherapy in NSCLC patients. Overall, 4 prospective studies and 5 retrospective studies were included.