Page 21 - Read Online
P. 21
Pellerino et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:41 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.80 Page 3 of 20
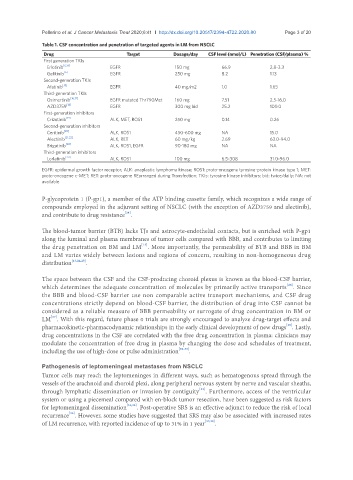
Table 1. CSF concentration and penetration of targeted agents in LM from NSCLC
Drug Target Dosage/day CSF level (nmol/L) Penetration (CSF/plasma) %
First generation TKIs
Erlotinib [6,14] EGFR 150 mg 66.9 2.8-3.3
Gefitinib [6] EGFR 250 mg 8.2 1.13
Second-generation TKIs
Afatinib [15] EGFR 40 mg/m2 1.0 1.65
Third-generation TKIs
Osimertinib [16,17] EGFR mutated Thr790Met 160 mg 7.51 2.5-16.0
AZD3759 [18] EGFR 300 mg bid 25.2 100.0
First-generation inhibitors
Crizotinib [19] ALK, MET, ROS1 250 mg 0.14 0.26
Second-generation inhibitors
Ceritinib [20] ALK, ROS1 450-600 mg NA 15.0
Alectinib [21,22] ALK, RET 60 mg/kg 2.69 63.0-94.0
Brigatinib [20] ALK, ROS1, EGFR 90-180 mg NA NA
Third-generation inhibitors
Lorlatinib [23] ALK, ROS1 100 mg 6.5-308 31.0-96.0
EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; ALK: anaplastic lymphoma kinase; ROS1: proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase type 1; MET:
proto-oncogene c-MET; RET: proto-oncogene REarranged during Transfection; TKIs: tyrosine kinase inhibitors; bid: twice/daily; NA: not
available
P-glycoprotein 1 (P-gp1), a member of the ATP binding cassette family, which recognizes a wide range of
compounds employed in the adjuvant setting of NSCLC (with the exception of AZD3759 and alectinib),
[24]
and contribute to drug resistance .
The blood-tumor barrier (BTB) lacks TJs and astrocyte-endothelial contacts, but is enriched with P-gp1
along the luminal and plasma membranes of tumor cells compared with BBB, and contributes to limiting
[13]
the drug penetration on BM and LM . More importantly, the permeability of BTB and BBB in BM
and LM varies widely between lesions and regions of concern, resulting in non-homogeneous drug
distribution [13,24,25] .
The space between the CSF and the CSF-producing choroid plexus is known as the blood-CSF barrier,
which determines the adequate concentration of molecules by primarily active transports . Since
[26]
the BBB and blood-CSF barrier use non comparable active transport mechanisms, and CSF drug
concentrations strictly depend on blood-CSF barrier, the distribution of drug into CSF cannot be
considered as a reliable measure of BBB permeability or surrogate of drug concentration in BM or
LM . With this regard, future phase 0 trials are strongly encouraged to analyze drug-target effects and
[27]
[28]
pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships in the early clinical development of new drugs . Lastly,
drug concentrations in the CSF are correlated with the free drug concentration in plasma: clinicians may
modulate the concentration of free drug in plasma by changing the dose and schedules of treatment,
including the use of high-dose or pulse administration [29-32] .
Pathogenesis of leptomeningeal metastases from NSCLC
Tumor cells may reach the leptomeninges in different ways, such as hematogenous spread through the
vessels of the arachnoid and choroid plexi, along peripheral nervous system by nerve and vascular sheaths,
[33]
through lymphatic dissemination or invasion by contiguity . Furthermore, access of the ventricular
system or using a piecemeal compared with en-block tumor resection, have been suggested as risk factors
for leptomeningeal dissemination [34,35] . Post-operative SRS is an effective adjunct to reduce the risk of local
recurrence . However, some studies have suggested that SRS may also be associated with increased rates
[36]
of LM recurrence, with reported incidence of up to 31% in 1 year [37,38] .