Page 87 - Read Online
P. 87
Page 6 of 9 Lo Re et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:17 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.11
A
B
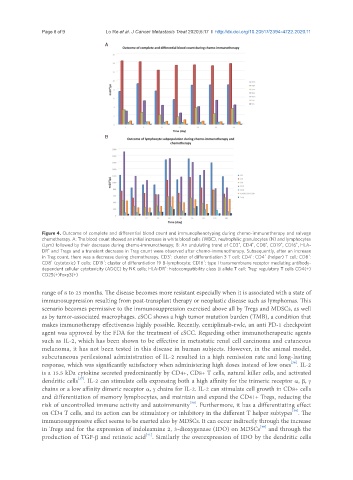
Figure 4. Outcome of complete and differential blood count and immunophenotyping during chemo-immunotherapy and salvage
chemotherapy. A: The blood count showed an initial increase in white blood cells (WBC), neutrophilic granulocytes (N) and lymphocytes
+
+
+
(Lym) followed by their decrease during chemo-immunotherapy; B: An undulating trend of CD3 , CD4 , CD8 , CD19 , CD16 , HLA-
+
+
DR and Tregs and a transient decrease in Treg count were observed after chemo-immunotherapy. Subsequently, after an increase
+
+
in Treg count, there was a decrease during chemotherapy. CD3 : cluster of differentiation 3 T cell; CD4 : CD4 (helper) T cell; CD8 :
+
+
+
+
+
CD8 (cytotoxic) T cells; CD19 : cluster of differentiation 19 B-lymphocyte; CD16 : type I transmembrane receptor mediating antibody-
+
dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) by NK cells; HLA-DR : histocompatibility class II allele T cell; Treg: regulatory T cells CD4(+)
+
CD25(+)Foxp3(+)
range of 8 to 25 months. The disease becomes more resistant especially when it is associated with a state of
immunosuppression resulting from post-transplant therapy or neoplastic disease such as lymphomas. This
scenario becomes permissive to the immunosuppression exercised above all by Tregs and MDSCs, as well
as by tumor-associated macrophages. cSCC shows a high tumor mutation burden (TMB), a condition that
makes immunotherapy effectiveness highly possible. Recently, cemiplimab-rwlc, an anti PD-1 checkpoint
agent was approved by the FDA for the treatment of cSCC. Regarding other immunotherapeutic agents
such as IL-2, which has been shown to be effective in metastatic renal cell carcinoma and cutaneous
melanoma, it has not been tested in this disease in human subjects. However, in the animal model,
subcutaneous perilesional administration of IL-2 resulted in a high remission rate and long-lasting
response, which was significantly satisfactory when administering high doses instead of low ones . IL-2
[36]
is a 15.5 kDa cytokine secreted predominantly by CD4+, CD8+ T cells, natural killer cells, and activated
dendritic cells . IL-2 can stimulate cells expressing both a high affinity for the trimeric receptor α, β, γ
[37]
chains or a low affinity dimeric receptor α, γ chains for IL-2. IL-2 can stimulate cell growth in CD8+ cells
and differentiation of memory lymphocytes, and maintain and expand the CD41+ Tregs, reducing the
[38]
risk of uncontrolled immune activity and autoimmunity . Furthermore, it has a differentiating effect
[39]
on CD4 T cells, and its action can be stimulatory or inhibitory in the different T helper subtypes . The
immunosuppressive effect seems to be exerted also by MDSCs. It can occur indirectly through the increase
in Tregs and for the expression of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) on MDSCs and through the
[40]
[41]
production of TGF-β and retinoic acid . Similarly the overexpression of IDO by the dendritic cells