Page 417 - Read Online
P. 417
Droste et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2023;9:2 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2022.94 Page 13 of 22
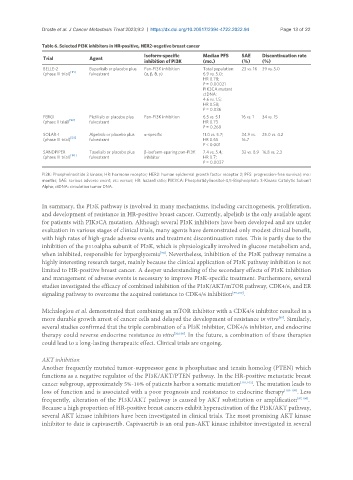
Table 6. Selected PI3K inhibitors in HR-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer
Isoform-specific Median PFS SAE Discontinuation rate
Trial Agent
inhibition of PI3K (mo.) (%) (%)
BELLE-2 Buparlisib or placebo plus Pan-PI3K inhibition Total population: 23 vs. 16 39 vs. 5.0
(phase III trial) [91] fulvestrant (α, β, δ, γ) 6.9 vs. 5.0;
HR 0.78;
P = 0.00021
PIK3CA mutant
ctDNA:
4.6 vs. 1.5;
HR 0.58;
P = 0.036
FERGI Pictilisib or placebo plus Pan-PI3K inhibition 6.5 vs. 5.1 16 vs. 1 34 vs. 15
(phase II trial) [92] fulvestrant HR 0.73
P = 0.268
SOLAR-1 Alpelisib or placebo plus α-specific 11.0 vs. 5.7; 34.9 vs. 25.0 vs. 4.2
[93]
(phase III trial) fulvestrant HR 0.65 16.7
P < 0.001
SANDPIPER Taselisib or placebo plus β-isoform-sparing pan-PI3K 7.4 vs. 5.4; 32 vs. 8.9 16.8 vs. 2.3
[90]
(phase III trial) fulvestrant inhibitor HR 0.7;
P = 0.0037
PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3 kinase; HR: hormone receptor; HER2: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; PFS: progression-free survival; mo.:
months; SAE: serious adverse event; vs.: versus; HR: hazard ratio; PIK3CA: Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase Catalytic Subunit
Alpha; ctDNA: circulation tumor DNA.
In summary, the PI3K pathway is involved in many mechanisms, including carcinogenesis, proliferation,
and development of resistance in HR-positive breast cancer. Currently, alpelisib is the only available agent
for patients with PIK3CA mutation. Although several PI3K inhibitors have been developed and are under
evaluation in various stages of clinical trials, many agents have demonstrated only modest clinical benefit,
with high rates of high-grade adverse events and treatment discontinuation rates. This is partly due to the
inhibition of the p110alpha subunit of PI3K, which is physiologically involved in glucose metabolism and,
when inhibited, responsible for hyperglycemia . Nevertheless, inhibition of the PI3K pathway remains a
[98]
highly interesting research target, mainly because the clinical application of PI3K pathway inhibition is not
limited to HR-positive breast cancer. A deeper understanding of the secondary effects of PI3K inhibition
and management of adverse events is necessary to improve PI3K-specific treatment. Furthermore, several
studies investigated the efficacy of combined inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, CDK4/6, and ER
signaling pathway to overcome the acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition [99,100] .
Michaloglou et al. demonstrated that combining an mTOR inhibitor with a CDK4/6 inhibitor resulted in a
more durable growth arrest of cancer cells and delayed the development of resistance in vitro . Similarly,
[99]
several studies confirmed that the triple combination of a PI3K inhibitor, CDK4/6 inhibitor, and endocrine
therapy could reverse endocrine resistance in vitro [30,100] . In the future, a combination of these therapies
could lead to a long-lasting therapeutic effect. Clinical trials are ongoing.
AKT inhibition
Another frequently mutated tumor-suppressor gene is phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) which
functions as a negative regulator of the PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway. In the HR-positive metastatic breast
cancer subgroup, approximately 5%-10% of patients harbor a somatic mutation [101,102] . The mutation leads to
loss of function and is associated with a poor prognosis and resistance to endocrine therapy [103-105] . Less
frequently, alteration of the PI3K/AKT pathway is caused by AKT substitution or amplification [87,106] .
Because a high proportion of HR-positive breast cancers exhibit hyperactivation of the PI3K/AKT pathway,
several AKT kinase inhibitors have been investigated in clinical trials. The most promising AKT kinase
inhibitor to date is capivasertib. Capivasertib is an oral pan-AKT kinase inhibitor investigated in several