Page 252 - Read Online
P. 252
Page 12 of 18 D'Angelo et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:30 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.86
A B
C D
E
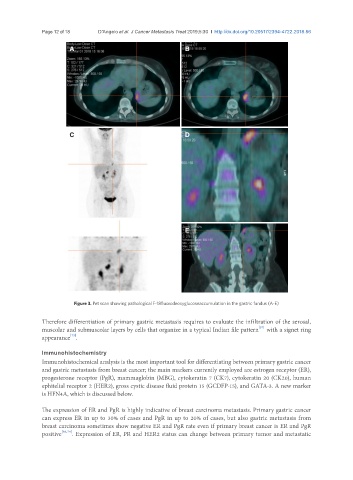
Figure 3. Pet scan showing pathological F-18fluorodeoxyglucoseaccumulation in the gastric fundus (A-E)
Therefore differentiation of primary gastric metastasis requires to evaluate the infiltration of the serosal,
[57]
muscolar and submuscolar layers by cells that organize in a typical Indian file pattern with a signet ring
[73]
appearance .
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemical analysis is the most important tool for differentiating between primary gastric cancer
and gastric metastasis from breast cancer; the main markers currently employed are estrogen receptor (ER),
progesterone receptor (PgR), mammaglobin (MBG), cytokeratin 7 (CK7), cytokeratin 20 (CK20), human
ephitelial receptor 2 (HER2), gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15), and GATA-3. A new marker
is HFN4A, which is discussed below.
The expression of ER and PgR is highly indicative of breast carcinoma metastasis. Primary gastric cancer
can express ER in up to 30% of cases and PgR in up to 20% of cases, but also gastric metastasis from
breast carcinoma sometimes show negative ER and PgR rate even if primary breast cancer is ER and PgR
positive [66,74] . Expression of ER, PR and HER2 status can change between primary tumor and metastatic