Page 149 - Read Online
P. 149
Park et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:17 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.84 Page 9 of 12
A
B C
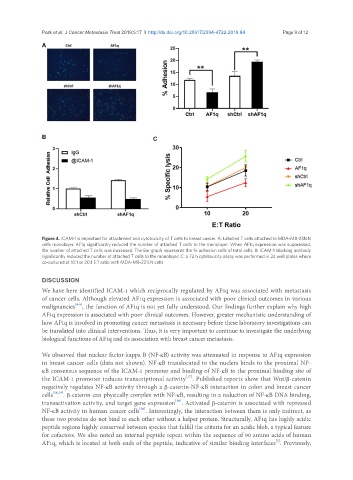
Figure 4. ICAM-1 is important for attachment and cytotoxicity of T cells to breast cancer. A: Labelled T cells attached to MDA-MB-231LN
cells monolayer. AF1q significantly reduced the number of attached T cells to the monolayer. When AF1q expression was suppressed,
the number of attached T cells was increased. The Bar graph represents the % adhesion cells of total cells; B: ICAM-1 blocking antibody
significantly reduced the number of attached T cells to the monolayer; C: a 72 h cytotoxicity assay was performed in 24 well plates where
co-cultured at 10:1 or 20:1 E:T ratio with MDA-MB-231LN cells
DISCUSSION
We have here identified ICAM-1 which reciprocally regulated by AF1q was associated with metastasis
of cancer cells. Although elevated AF1q expression is associated with poor clinical outcomes in various
[4-6]
malignancies , the function of AF1q is not yet fully understood. Our findings further explain why high
AF1q expression is associated with poor clinical outcomes. However, greater mechanistic understanding of
how AF1q is involved in promoting cancer metastasis is necessary before these laboratory investigations can
be translated into clinical interventions. Thus, it is very important to continue to investigate the underlying
biological functions of AF1q and its association with breast cancer metastasis.
We observed that nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activity was attenuated in response to AF1q expression
in breast cancer cells (data not shown). NF-κB translocated to the nuclers binds to the proximal NF-
κB consensus sequence of the ICAM-1 promoter and binding of NF-κB to the proximal binding site of
[17]
the ICAM-1 promoter induces transcriptional activity . Published reports show that Wnt/β-catenin
negatively regulates NF-κB activity through a β-catenin-NF-κB interaction in colon and breast cancer
cells [18,19] . β-catenin can physically complex with NF-κB, resulting in a reduction of NF-κB DNA binding,
[20]
transactivation activity, and target gene expression . Activated β-catenin is associated with repressed
[20]
NF-κB activity in human cancer cells . Interestingly, the interaction between them is only indirect, as
these two proteins do not bind to each other without a helper protein. Structurally, AF1q has highly acidic
peptide regions highly conserved between species that fulfill the criteria for an acidic blob, a typical feature
for cofactors. We also noted an internal peptide repeat within the sequence of 90 amino acids of human
[2]
AF1q, which is located at both ends of the peptide, indicative of similar binding interfaces . Previously,