Page 8 - Read Online
P. 8
Wartena et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:59 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.66 Page 3 of 8
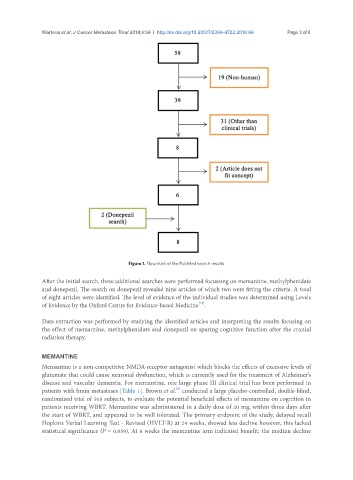
Figure 1. Flowchart of the PubMed search results
After the initial search, three additional searches were performed focussing on memantine, methylphenidate
and donepezil. The search on donepezil revealed nine articles of which two were fitting the criteria. A total
of eight articles were identified. The level of evidence of the individual studies was determined using Levels
[12]
of Evidence by the Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine .
Data extraction was performed by studying the identified articles and interpreting the results focusing on
the effect of memantine, methylphenidate and donepezil on sparing cognitive function after the cranial
radiation therapy.
MEMANTINE
Memantine is a non-competitive NMDA-receptor antagonist which blocks the effects of excessive levels of
glutamate that could cause neuronal dysfunction, which is currently used for the treatment of Alzheimer’s
disease and vascular dementia. For memantine, one large phase III clinical trial has been performed in
[6]
patients with brain metastases [Table 1]. Brown et al. conducted a large placebo-controlled, double-blind,
randomized trial of 508 subjects, to evaluate the potential beneficial effects of memantine on cognition in
patients receiving WBRT. Memantine was administered in a daily dose of 20 mg, within three days after
the start of WBRT, and appeared to be well tolerated. The primary endpoint of the study, delayed recall
Hopkins Verbal Learning Test - Revised (HVLT-R) at 24 weeks, showed less decline however, this lacked
statistical significance (P = 0.059). At 8 weeks the memantine arm indicated benefit; the median decline