Page 63 - Read Online
P. 63
Page 8 of 16 Enrique et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:54 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.20
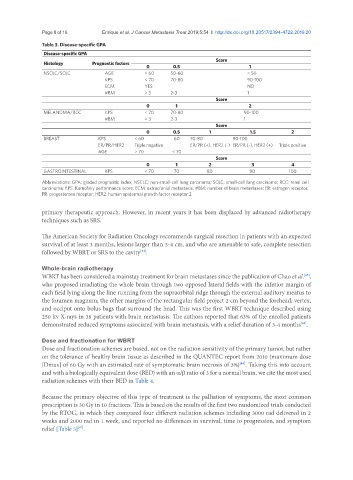
Table 3. Disease-specific GPA
Disease-specific GPA
Score
Histology Prognostic factors
0 0.5 1
NSCLC/SCLC AGE > 60 50-60 < 50
KPS < 70 70-80 90-100
ECM YES NO
#BM > 3 2-3 1
Score
0 1 2
MELANOMA/RCC KPS < 70 70-80 90-100
#BM > 3 2-3 1
Score
0 0.5 1 1.5 2
BREAST KPS < 60 60 70-80 90-100
ER/PR/HER2 Triple negative ER/PR (+), HER2 (-) ER/PR (-), HER2 (+) Triple positive
AGE > 70 < 70
Score
0 1 2 3 4
GASTROINTESTINAL KPS < 70 70 80 90 100
Abbreviations: GPA: graded prognostic index; NSCLC: non-small-cell lung carcinoma; SCLC: small-cell lung carcinoma; RCC: renal cell
carcinoma; KPS: Karnofsky performance score; ECM: extracranial metastasis; #BM: number of brain metastases; ER: estrogen receptor;
PR: progesterone receptor; HER2: human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
primary therapeutic approach. However, in recent years it has been displaced by advanced radiotherapy
techniques such as SRS.
The American Society for Radiation Oncology recommends surgical resection in patients with an expected
survival of at least 3 months, lesions larger than 3-4 cm, and who are amenable to safe, complete resection
followed by WBRT or SRS to the cavity .
[44]
Whole-brain radiotherapy
WBRT has been considered a mainstay treatment for brain metastases since the publication of Chao et al. ,
[45]
who proposed irradiating the whole brain through two opposed lateral fields with the inferior margin of
each field lying along the line running from the supraorbital ridge through the external auditory meatus to
the foramen magnum; the other margins of the rectangular field project 2 cm beyond the forehead, vertex,
and occiput onto bolus bags that surround the head. This was the first WBRT technique described using
250 kv X-rays in 38 patients with brain metastasis. The authors reported that 63% of the enrolled patients
demonstrated reduced symptoms associated with brain metastasis, with a relief duration of 3-4 months .
[45]
Dose and fractionation for WBRT
Dose and fractionation schemes are based, not on the radiation sensitivity of the primary tumor, but rather
on the tolerance of healthy brain tissue as described in the QUANTEC report from 2010 (maximum dose
[Dmax] of 60 Gy with an estimated rate of symptomatic brain necrosis of 3%) . Taking this into account
[46]
and with a biologically equivalent dose (BED) with an α/β ratio of 3 for a normal brain, we cite the most used
radiation schemes with their BED in Table 4.
Because the primary objective of this type of treatment is the palliation of symptoms, the most common
prescription is 30 Gy in 10 fractions. This is based on the results of the first two randomized trials conducted
by the RTOG, in which they compared four different radiation schemes including 3000 rad delivered in 2
weeks and 2000 rad in 1 week, and reported no differences in survival, time to progression, and symptom
relief [Table 5] .
[47]