Page 41 - Read Online
P. 41
Dumane et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:42 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.08 Page 7 of 10
B
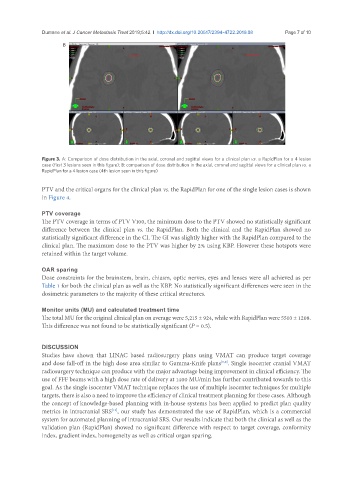
Figure 3. A: Comparison of dose distribution in the axial, coronal and sagittal views for a clinical plan vs. a RapidPlan for a 4 lesion
case (first 3 lesions seen in this figure); B: comparison of dose distribution in the axial, coronal and sagittal views for a clinical plan vs. a
RapidPlan for a 4 lesion case (4th lesion seen in this figure)
PTV and the critical organs for the clinical plan vs. the RapidPlan for one of the single lesion cases is shown
in Figure 4.
PTV coverage
The PTV coverage in terms of PTV V100, the minimum dose to the PTV showed no statistically significant
difference between the clinical plan vs. the RapidPlan. Both the clinical and the RapidPlan showed no
statistically significant difference in the CI. The GI was slightly higher with the RapidPlan compared to the
clinical plan. The maximum dose to the PTV was higher by 2% using KBP. However these hotspots were
retained within the target volume.
OAR sparing
Dose constraints for the brainstem, brain, chiasm, optic nerves, eyes and lenses were all achieved as per
Table 1 for both the clinical plan as well as the KBP. No statistically significant differences were seen in the
dosimetric parameters to the majority of these critical structures.
Monitor units (MU) and calculated treatment time
The total MU for the original clinical plan on average were 5,215 ± 924, while with RapidPlan were 5503 ± 1208.
This difference was not found to be statistically significant (P = 0.5).
DISCUSSION
Studies have shown that LINAC based radiosurgery plans using VMAT can produce target coverage
[5,6]
and dose fall-off in the high dose area similar to Gamma-Knife plans . Single isocenter cranial VMAT
radiosurgery technique can produce with the major advantage being improvement in clinical efficiency. The
use of FFF beams with a high dose rate of delivery at 1400 MU/min has further contributed towards to this
goal. As the single isocenter VMAT technique replaces the use of multiple isocenter techniques for multiple
targets, there is also a need to improve the efficiency of clinical treatment planning for these cases. Although
the concept of knowledge-based planning with in-house systems has been applied to predict plan quality
[12]
metrics in intracranial SRS , our study has demonstrated the use of RapidPlan, which is a commercial
system for automated planning of intracranial SRS. Our results indicate that both the clinical as well as the
validation plan (RapidPlan) showed no significant difference with respect to target coverage, conformity
index, gradient index, homogeneity as well as critical organ sparing.