Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Page 8 of 12 Khan et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:71 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2019.017
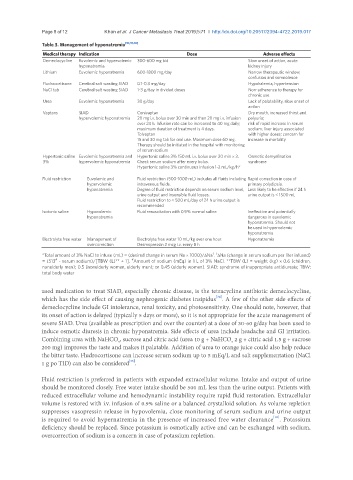
Table 3. Management of hyponatremia [10,19,46]
Medical therapy Indication Dose Adverse effects
Demeclocycline Euvolemic and hypervolemic 300-600 mg bid Slow onset of action, acute
hyponatremia kidney injury
Lithium Euvolemic hyponatremia 600-1800 mg/day Narrow therapeutic window,
confusion and somnolence
Fludrocortisone Cerebral salt wasting SIAD 0.1-0.3 mg/day Hypokalemia, hypertension
NaCl tab Cerebral salt wasting SIAD 1-3 g/day in divided doses Non-adherence to therapy for
chronic use
Urea Euvolemic hyponatremia 30 g/day Lack of palatability, slow onset of
action
Vaptans SIAD Conivaptan Dry mouth, increased thirst and
hypervolemic hyponatremia 20 mg i.v. bolus over 30 min and then 20 mg i.v. infusion polyuria;
over 24 h. Infusion rate can be increased to 40 mg daily; risk of rapid increase in serum
maximum duration of treatment is 4 days. sodium; liver injury associated
Tolvaptan with higher doses; concern for
15 and 30 mg tab for oral use. Maximum dose 60 mg. increase in mortality
Therapy should be initiated in the hospital with monitoring
of serum sodium
Hypertonic saline Euvolemic hyponatremia and Hypertonic saline 3% 150 mL i.v. bolus over 20 min × 3. Osmotic demyelination
3% hypervolemic hyponatremia Check serum sodium after every bolus. syndrome
Hypertonic saline 3% continuous infusion 1-2 mL/kg/h*
Fluid restriction Euvolemic and Fluid restriction (500-1000 mL) includes all fluids including Rapid correction in case of
hypervolemic intravenous fluids. primary polydipsia.
hyponatremia Degree of fluid restriction depends on serum sodium level, Less likely to be effective if 24 h
urine output and insensible fluid losses. urine output is < 1500 mL
Fluid restriction to < 500 mL/day of 24 h urine output is
recommended
Isotonic saline Hypovolemic Fluid resuscitation with 0.9% normal saline Ineffective and potentially
hyponatremia dangerous in euvolemic
hyponatremia. Should not
be used in hypervolemic
hyponatremia
Electrolyte free water Management of Electrolyte free water 10 mL/kg over one hour. Hyponatremia
overcorrection Desmopressin 2 mcg i.v. every 8 h
† †
*Total amount of 3% NaCl to infuse (mL) = (desired change in serum Na × 1000)/ΔNa . ΔNa (change in serum sodium per liter infused)
#
#
= (513 - serum sodium)/[TBW (L)** + 1]. Amount of sodium (mEq) in 1 L of 3% NaCl. **TBW (L) = weight (kg) × 0.6 (children,
nonelderly men); 0.5 (nonelderly women, elderly men); or 0.45 (elderly women). SIAD: syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis; TBW:
total body water
used medication to treat SIAD, especially chronic disease, is the tetracycline antibiotic demeclocycline,
[34]
which has the side effect of causing nephrogenic diabetes insipidus . A few of the other side effects of
demeclocycline include GI intolerance, renal toxicity, and photosensitivity. One should note, however, that
its onset of action is delayed (typically 5 days or more), so it is not appropriate for the acute management of
severe SIAD. Urea (available as prescription and over the counter) at a dose of 30-60 g/day has been used to
induce osmotic diuresis in chronic hyponatremia. Side effects of urea include headache and GI irritation.
Combining urea with NaHCO , sucrose and citric acid (urea 10 g + NaHCO 2 g + citric acid 1.5 g + sucrose
3
3
200 mg) improves the taste and makes it palatable. Addition of urea to orange juice could also help reduce
the bitter taste. Fludrocortisone can increase serum sodium up to 5 mEq/L and salt supplementation (NaCl
[35]
1 g po TID) can also be considered .
Fluid restriction is preferred in patients with expanded extracellular volume. Intake and output of urine
should be monitored closely. Free water intake should be 500 mL less than the urine output. Patients with
reduced extracellular volume and hemodynamic instability require rapid fluid restoration. Extracellular
volume is restored with i.v. infusion of 0.9% saline or a balanced crystalloid solution. As volume repletion
suppresses vasopressin release in hypovolemia, close monitoring of serum sodium and urine output
[10]
is required to avoid hypernatremia in the presence of increased free water clearance . Potassium
deficiency should be replaced. Since potassium is osmotically active and can be exchanged with sodium,
overcorrection of sodium is a concern in case of potassium repletion.