Page 13 - Read Online
P. 13
Spallanzani et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2018;4:28 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.31 Page 7 of 17
Hot tumors Cold tumors
CMS1: Immune CMS4: Mesenchymal CMS2: Canonical CMS3: Metabolic
Hypermutation Inflammation WNT and MYC activation KRAS mutations
dMMR Stromal infiltration
BRAF mutations Angiogenesis
TILs
NK cells TILs
Macrophages CAFs Poor immunogenicity
Cancer PD1 Cancer TGFβ
cells ↑↑ CTLA4 cells complement
IDO1
CXCR3/CCR5 CCL2
IFNγ CXCL12
Immunotherapy CHT + target therapy + immunotherapy?
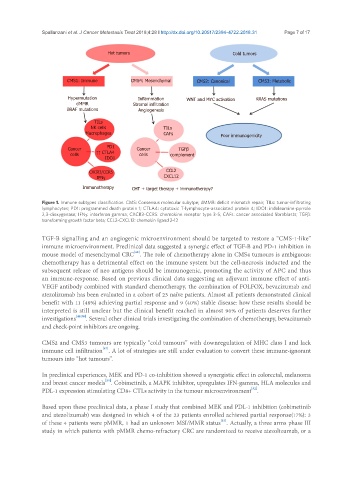
Figure 1. Immune subtypes classification. CMS: Consensus molecular subytpe; dMMR: deficit mismatch repair; TILs: tumor-infiltrating
lymphocytes; PD1: programmed death protein 1; CTLA4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; IDO1: indoleamine-pyrrole
2,3-dioxygenase; IFNg: interferon gamma; CXCR3-CCR5: chemokine receptor type 3-5; CAFs: cancer associated fibroblasts; TGFβ:
transforming growth factor beta; CCL2-CXCL12: chemokin ligand 2-12
TGF-B signalling and an angiogenic microenvironment should be targeted to restore a “CMS-1-like”
immune microenvironment. Preclinical data suggested a synergic effect of TGF-B and PD-1 inhibition in
[48]
mouse model of mesenchymal CRC . The role of chemotherapy alone in CMS4 tumours is ambiguous:
chemotherapy has a detrimental effect on the immune system but the cell-necrosis inducted and the
subsequent release of neo antigens should be immunogenic, promoting the activity of APC and thus
an immune-response. Based on previous clinical data suggesting an adjuvant immune effect of anti-
VEGF antibody combined with standard chemotherapy, the combination of FOLFOX, bevacizumab and
atezolizumab has been evaluated in a cohort of 23 naïve patients. Almost all patients demonstrated clinical
benefit with 11 (48%) achieving partial response and 9 (40%) stable disease: how these results should be
interpreted is still unclear but the clinical benefit reached in almost 90% of patients deserves further
investigations [49,50] . Several other clinical trials investigating the combination of chemotherapy, bevacizumab
and check-point inhibitors are ongoing.
CMS2 and CMS3 tumours are typically “cold tumours” with downregulation of MHC class I and lack
[47]
immune cell infiltration . A lot of strategies are still under evaluation to convert these immune-ignorant
tumours into “hot tumours”.
In preclinical experiences, MEK and PD-1 co-inhibition showed a synergistic effect in colorectal, melanoma
[51]
and breast cancer models . Cobimetinib, a MAPK inhibitor, upregulates IFN-gamma, HLA molecules and
[52]
PDL-1 expression stimulating CD8+ CTLs activity in the tumour microenvironment .
Based upon these preclinical data, a phase I study that combined MEK and PDL-1 inhibition (cobimetinib
and atezolizumab) was designed in which 4 of the 23 patients enrolled achieved partial response(17%): 3
[53]
of these 4 patients were pMMR, 1 had an unknown MSI/MMR status . Actually, a three arms phase III
study in which patients with pMMR chemo-refractory CRC are randomized to receive atezolizumab, or a