Page 8 - Read Online
P. 8
Mason What clinicians should want from scientists
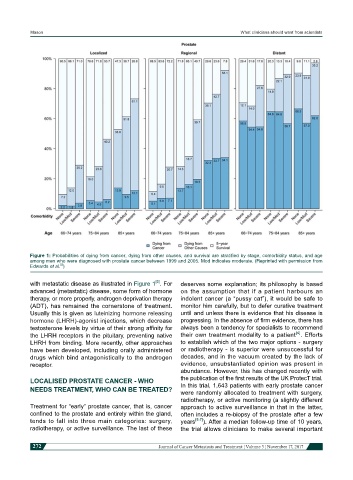
Figure 1: Probabilities of dying from cancer, dying from other causes, and survival are stratified by stage, comorbidity status, and age
among men who were diagnosed with prostate cancer between 1999 and 2005. Mod indicates moderate. (Reprinted with permission from
[3]
Edwards et al. )
[3]
with metastatic disease as illustrated in Figure 1 . For deserves some explanation; its philosophy is based
advanced (metastatic) disease, some form of hormone on the assumption that if a patient harbours an
therapy, or more properly, androgen deprivation therapy indolent cancer (a “pussy cat”), it would be safe to
(ADT), has remained the cornerstone of treatment. monitor him carefully, but to defer curative treatment
Usually this is given as luteinizing hormone releasing until and unless there is evidence that his disease is
hormone (LHRH)-agonist injections, which decrease progressing. In the absence of firm evidence, there has
testosterone levels by virtue of their strong affinity for always been a tendency for specialists to recommend
[4]
the LHRH receptors in the pituitary, preventing native their own treatment modality to a patient . Efforts
LHRH from binding. More recently, other approaches to establish which of the two major options - surgery
have been developed, including orally administered or radiotherapy - is superior were unsuccessful for
drugs which bind antagonistically to the androgen decades, and in the vacuum created by the lack of
receptor. evidence, unsubstantiated opinion was present in
abundance. However, this has changed recently with
LOCALISED PROSTATE CANCER - WHO the publication of the first results of the UK ProtecT trial.
NEEDS TREATMENT, WHO CAN BE TREATED? In this trial, 1,643 patients with early prostate cancer
were randomly allocated to treatment with surgery,
radiotherapy, or active monitoring (a slightly different
Treatment for “early” prostate cancer, that is, cancer approach to active surveillance in that in the latter,
confined to the prostate and entirely within the gland, often includes a re-biopsy of the prostate after a few
tends to fall into three main categories: surgery, years [5-7] ). After a median follow-up time of 10 years,
radiotherapy, or active surveillance. The last of these the trial allows clinicians to make several important
272 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ November 17, 2017