Page 124 - Read Online
P. 124
Ibrahim et al ALDHs and prostate cancer
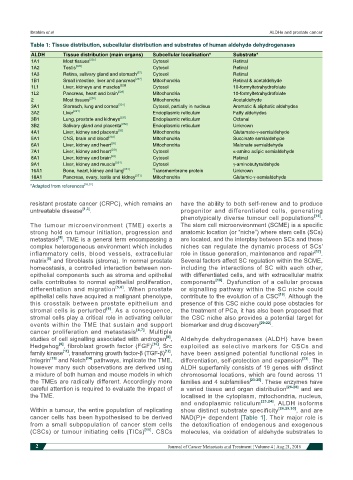
Table 1: Tissue distribution, subcellular distribution and substrates of human aldehyde dehydrogenases
ALDH Tissue distribution (main organs) Subcellular localisation* Substrate*
1A1 Most tissues [225] Cytosol Retinal
1A2 Testis [226] Cytosol Retinal
1A3 Retina, salivary gland and stomach [87] Cytosol Retinal
1B1 Small intestine, liver and pancreas [227] Mitochondria Retinal & acetaldehyde
1L1 Liver, kidneys and muscles [228] Cytosol 10-formyltetrahydrofolate
1L2 Pancreas, heart and brain [229] Mitochondria 10-formyltetrahydrofolate
2 Most tissues [230] Mitochondria Acetaldehyde
3A1 Stomach, lung and cornea [231] Cytosol, partially in nucleus Aromatic & aliphatic aldehydes
3A2 Liver [231] Endoplasmic reticulum Fatty aldehydes
3B1 Lung, prostate and kidneys [231] Endoplasmic reticulum Octanal
3B2 Salivary gland and placenta [232] Endoplasmic reticulum Unknown
4A1 Liver, kidney and placenta [26] Mitochondria Glutamate-γ-semialdehyde
5A1 CNS, brain and blood [233] Mitochondria Succinate semialdehyde
6A1 Liver, kidney and heart [26] Mitochondria Malonate semialdehyde
7A1 Liver, kidney and heart [231] Cytosol α-amino adipic semialdehyde
8A1 Liver, kidney and brain [26] Cytosol Retinal
9A1 Liver, kidney and muscle [231] Cytosol γ-aminobutyraldehyde
16A1 Bone, heart, kidney and lung [231] Transmembrane protein Unknown
18A1 Pancreas, ovary, testis and kidney [231] Mitochondria Glutamic-γ-semialdehyde
*Adapted from references [26,32]
resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), which remains an have the ability to both self-renew and to produce
untreatable disease [1,3] . progenitor and differentiated cells, generating
phenotypically diverse tumour cell populations [16] .
The tumour microenvironment (TME) exerts a The stem cell microenvironment (SCME) is a specific
strong hold on tumour initiation, progression and anatomic location (or “niche”) where stem cells (SCs)
[4]
metastasis . TME is a general term encompassing a are located, and the interplay between SCs and these
complex heterogeneous environment which includes niches can regulate the dynamic process of SCs’
inflammatory cells, blood vessels, extracellular role in tissue generation, maintenance and repair [17] .
[5]
matrix and fibroblasts (stroma). In normal prostate Several factors affect SC regulation within the SCME,
homeostasis, a controlled interaction between non- including the interactions of SC with each other,
epithelial components such as stroma and epithelial with differentiated cells, and with extracellular matrix
cells contributes to normal epithelial proliferation, components [18] . Dysfunction of a cellular process
differentiation and migration [5,6] . When prostate or signalling pathway within the SC niche could
epithelial cells have acquired a malignant phenotype, contribute to the evolution of a CSC [19] . Although the
this crosstalk between prostate epithelium and presence of this CSC niche could pose obstacles for
[6]
stromal cells is perturbed . As a consequence, the treatment of PCa, it has also been proposed that
stromal cells play a critical role in activating cellular the CSC niche also provides a potential target for
events within the TME that sustain and support biomarker and drug discovery [20-22] .
cancer proliferation and metastasis [4,7] . Multiple
[8]
studies of cell signalling associated with androgen , Aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDH) have been
[9]
Hedgehog , fibroblast growth factor (FGF) [10] , Src exploited as selective markers for CSCs and
[11]
family kinase , transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) , have been assigned potential functional roles in
[12]
Integrin [13] and Notch [14] pathways, implicate the TME, differentiation, self-protection and expansion [23] . The
however many such observations are derived using ALDH superfamily consists of 19 genes with distinct
a mixture of both human and mouse models in which chromosomal locations, which are found across 11
the TMEs are radically different. Accordingly more families and 4 subfamilies [23-25] . These enzymes have
careful attention is required to evaluate the impact of a varied tissue and organ distribution [26-28] and are
the TME. localised in the cytoplasm, mitochondria, nucleus,
and endoplasmic reticulum [23,24] . ALDH isoforms
Within a tumour, the entire population of replicating show distinct substrate specificity [26,29,30] , and are
cancer cells has been hypothesised to be derived NAD(P)+ dependent [Table 1]. Their major role is
from a small subpopulation of cancer stem cells the detoxification of endogenous and exogenous
(CSCs) or tumour initiating cells (TICs) [15] . CSCs molecules, via oxidation of aldehyde substrates to
2 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 4 ¦ Aug 21, 2018