Page 128 - Read Online
P. 128
Ibrahim et al ALDHs and prostate cancer
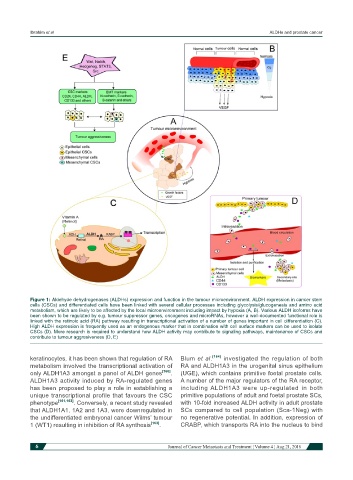
Figure 1: Aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDHs) expression and function in the tumour microenvironment. ALDH expression in cancer stem
cells (CSCs) and differentiated cells have been linked with several cellular processes including glycolysis/glucogenesis and amino acid
metabolism, which are likely to be affected by the local microenvironment including impact by hypoxia (A, B). Various ALDH isoforms have
been shown to be regulated by e.g. tumour suppressor genes, oncogenes and microRNAs, however a well-documented functional role is
linked with the retinoic acid (RA) pathway resulting in transcriptional activation of a number of genes important in cell differentiation (C).
High ALDH expression is frequently used as an endogenous marker that in combination with cell surface markers can be used to isolate
CSCs (D). More research is required to understand how ALDH activity may contribute to signaling pathways, maintenance of CSCs and
contribute to tumour aggresiveness (D, E)
keratinocytes, it has been shown that regulation of RA Blum et al. [164] investigated the regulation of both
metabolism involved the transcriptional activation of RA and ALDH1A3 in the urogenital sinus epithelium
only ALDH1A3 amongst a panel of ALDH genes [160] . (UGE), which contains primitive foetal prostate cells.
ALDH1A3 activity induced by RA-regulated genes A number of the major regulators of the RA receptor,
has been proposed to play a role in establishing a including ALDH1A3 were up-regulated in both
unique transcriptional profile that favours the CSC primitive populations of adult and foetal prostate SCs,
phenotype [161,162] . Conversely, a recent study revealed with 10-fold increased ALDH activity in adult prostate
that ALDH1A1, 1A2 and 1A3, were downregulated in SCs compared to cell population (Sca-1Neg) with
the undifferentiated embryonal cancer Wilms’ tumour no regenerative potential. In addition, expression of
1 (WT1) resulting in inhibition of RA synthesis [163] . CRABP, which transports RA into the nucleus to bind
6 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 4 ¦ Aug 21, 2018