Page 13 - Read Online
P. 13
Ji et al. Intell Robot 2021;1(2):151-75 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2021.14 Page 157
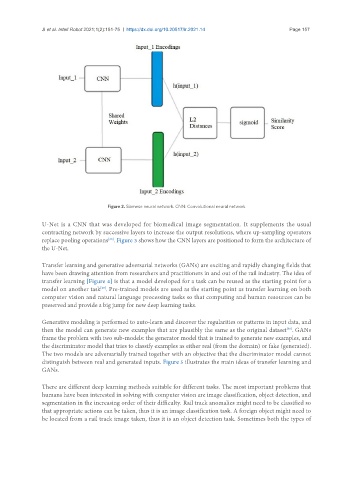
Figure 2. Siamese neural network. CNN: Convolutional neural network
U-Net is a CNN that was developed for biomedical image segmentation. It supplements the usual
contracting network by successive layers to increase the output resolutions, where up-sampling operators
[28]
replace pooling operations . Figure 3 shows how the CNN layers are positioned to form the architecture of
the U-Net.
Transfer learning and generative adversarial networks (GANs) are exciting and rapidly changing fields that
have been drawing attention from researchers and practitioners in and out of the rail industry. The idea of
transfer learning [Figure 4] is that a model developed for a task can be reused as the starting point for a
[29]
model on another task . Pre-trained models are used as the starting point as transfer learning on both
computer vision and natural language processing tasks so that computing and human resources can be
preserved and provide a big jump for new deep learning tasks.
Generative modeling is performed to auto-learn and discover the regularities or patterns in input data, and
then the model can generate new examples that are plausibly the same as the original dataset . GANs
[30]
frame the problem with two sub-models: the generator model that is trained to generate new examples, and
the discriminator model that tries to classify examples as either real (from the domain) or fake (generated).
The two models are adversarially trained together with an objective that the discriminator model cannot
distinguish between real and generated inputs. Figure 5 illustrates the main ideas of transfer learning and
GANs.
There are different deep learning methods suitable for different tasks. The most important problems that
humans have been interested in solving with computer vision are image classification, object detection, and
segmentation in the increasing order of their difficulty. Rail track anomalies might need to be classified so
that appropriate actions can be taken, thus it is an image classification task. A foreign object might need to
be located from a rail track image taken, thus it is an object detection task. Sometimes both the types of