Page 862 - Read Online
P. 862
Silk et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:73 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.61 Page 13 of 16
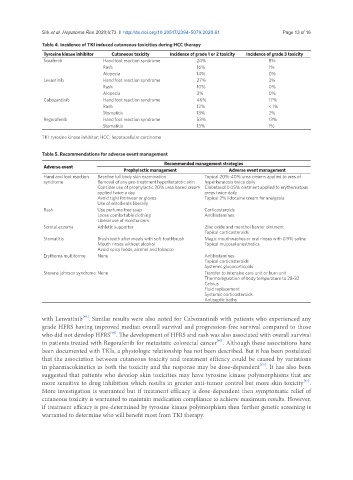
Table 4. Incidence of TKI induced cutaneous toxicities during HCC therapy
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor Cutaneous toxicity Incidence of grade 1 or 2 toxicity Incidence of grade 3 toxicity
Sorafenib Hand foot reaction syndrome 24% 8%
Rash 16% 1%
Alopecia 14% 0%
Levantinib Hand foot reaction syndrome 27% 3%
Rash 10% 0%
Alopecia 3% 0%
Cabozantinib Hand foot reaction syndrome 46% 17%
Rash 12% < 1%
Stomatitis 13% 2%
Regorafenib Hand foot reaction syndrome 53% 13%
Stomatitis 13% 1%
TKI: tyrosine kinase inhibitor; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
Table 5. Recommendations for adverse event management
Recommended management strategies
Adverse event
Prophylactic management Adverse event management
Hand and foot reaction Baseline full body skin examination Topical 20%-40% urea creams applied to ares of
syndrome Removal of any pre-treatment hyperkeratotic skin hyperkeratosis twice daily
Consider use of prophylactic 20% urea based cream Clobetasol 0.05% ointment applied to erythematous
applied twice a day areas twice daily
Avoid tight footwear or gloves Topical 2% lidocaine cream for analgesia
Use of emollients liberally
Rash Use perfume free soap Corticosteroids
Loose comfortable clothing Antihistamines
Liberal use of moisturizers
Scrotal eczema Athletic supporter Zinc oxide and menthol barrier ointment
Topical corticosteroids
Stomatitis Brush teeth after meals with soft toothbrush Magic mouthwashes or oral rinses with 0.9% saline
Mouth rinses without alcohol Topical mucosal anesthetics
Avoid spicy foods, alcohol and tobacco
Erythema multiforme None Antihistamines
Topical corticosteroids
Systemic glucocorticoids
Stevens johnson syndrome None Transfer to intensive care unit or burn unit
Thermoregulation of body temperature to 28-32
Celsius
Fluid replacement
Systemic corticosteroids
Antiseptic baths
[65]
with Lenvatinib . Similar results were also noted for Cabozantinib with patients who experienced any
grade HFRS having improved median overall survival and progression-free survival compared to those
[66]
who did not develop HFRS . The development of HFRS and rash was also associated with overall survival
in patients treated with Regorafenib for metastatic colorectal cancer . Although these associations have
[67]
been documented with TKIs, a physiologic relationship has not been described. But it has been postulated
that the association between cutaneous toxicity and treatment efficacy could be caused by variations
[65]
in pharmacokinetics as both the toxicity and the response may be dose-dependent . It has also been
suggested that patients who develop skin toxicities may have tyrosine kinase polymorphisms that are
[61]
more sensitive to drug inhibition which results in greater anti-tumor control but more skin toxicity .
More investigation is warranted but if treatment efficacy is dose-dependent then symptomatic relief of
cutaneous toxicity is warranted to maintain medication compliance to achieve maximum results. However,
if treatment efficacy is pre-determined by tyrosine kinase polymorphism then further genetic screening is
warranted to determine who will benefit most from TKI therapy.