Page 698 - Read Online
P. 698
Merle et al. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:60 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.52 Page 3 of 10
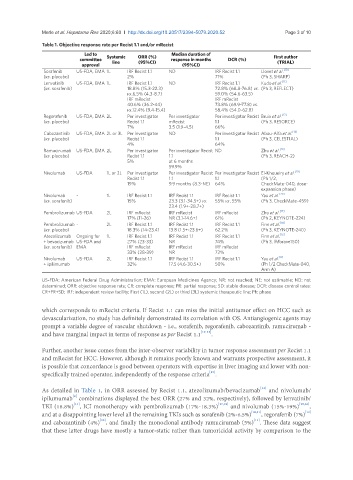
Table 1. Objective response rate per Recist 1.1 and/or mRecist
Led to Median duration of
committee Systemic ORR (%) response in months DCR (%) First author
approval line (95%CI) (95%CI) (TRIAL)
Sorafenib US-FDA, EMA 1L IRF Recist 1.1 ND IRF Recist 1.1 Llovet et al. [10]
(vs. placebo) 2% 71% (Ph 3, SHARP)
Lenvatinib US-FDA, EMA 1L IRF Recist 1.1 ND IRF Recist 1.1 Kudo et al. [11]
(vs. sorafenib) 18.8% (15.3-22.3) 72.8% (68.8-76.8) vs. (Ph 3, REFLECT)
vs.6.5% (4.3-8.7) 59.0% (54.6-63.5)
IRF mRecist IRF mRecist
40.6% (36.2-44) 73.8% (69.9-77.8) vs.
vs.12.4% (9.4-15.4) 58.4% (54.0-62.8)
Regorafenib US-FDA, EMA 2L Per investigator Per investigator Per investigator Recist Bruix et al. [12]
(vs. placebo) Recist 1.1 mRecist 1.1 (Ph 3, RESORCE)
7% 3.5 (1.9-4.5) 66%
Cabozantinib US-FDA, EMA 2L or 3L Per investigator ND Per investigator Recist Abou-Alfa et al. [13]
(vs. placebo) Recist 1.1 1.1 (Ph 3, CELESTIAL)
4% 64%
Ramucirumab US-FDA, EMA 2L Per investigator Per investigator Recist ND Zhu et al. [14]
(vs. placebo) Recist 1.1 1.1 (Ph 3, REACH-2)
5% at 6 months
59.9%
Nivolumab US-FDA 1L or 2L Per investigator Per investigator Recist Per investigator Recist El-Khoueiry et al. [19]
Recist 1.1 1.1 1.1 (Ph 1/2,
19% 9.9 months (8.3-NE) 64% CheckMate-040, dose-
expansion phase)
Nivolumab - 1L IRF Recist 1.1 IRF Recist 1.1 IRF Recist 1.1 Yau et al. [20]
(vs. sorafenib) 15% 23.3 (3.1-34.5+) vs. 55% vs. 55% (Ph 3, CheckMate-459)
23.4 (1.9+-28.7+)
Pembrolizumab US-FDA 2L IRF mRecist IRF mRecist IRF mRecist Zhu et al. [17]
17% (11-26) NR (3.1-14.6+) 61% (Ph 2, KEYNOTE-224)
Pembrolizumab - 2L IRF Recist 1.1 IRF Recist 1.1 IRF Recist 1.1 Finn et al. [18]
(vs. placebo) 18.3% (14-23.4) 13.8 (1.5+-23.6+) 62.2% (Ph 3, KEYNOTE-240)
Atezolizumab Ongoing for 1L IRF Recist 1.1 IRF Recist 1.1 IRF Recist 1.1 Finn et al. [16]
+ bevacizumab US-FDA and 27% (23-33) NR 74% (Ph 3, IMbrave150)
(vs. sorafenib) EMA IRF mRecist IRF mRecist IRF mRecist
33% (28-39) NR 72%
Nivolumab US-FDA 2L IRF Recist 1.1 IRF Recist 1.1 IRF Recist 1.1 Yau et al. [8]
+ ipilimumab 32% 17.5 (4.6-30.5+) 50% (Ph 1/2 CheckMate-040,
Arm A)
US-FDA: American Federal Drug Administration; EMA: European Medicines Agency; NR: not reached; NE: not estimable; ND: not
determined; ORR: objective response rate; CR: complete response; PR: partial response; SD: stable disease; DCR: disease control rates:
CR+PR+SD; IRF: independent review facility; First (1L), second (2L) or third (3L) systemic therapeutic line; Ph: phase
which corresponds to mRecist criteria. If Recist 1.1 can miss the initial antitumor effect on HCC such as
devascularization, no study has definitely demonstrated its correlation with OS. Antiangiogenic agents may
prompt a variable degree of vascular shutdown - i.e., sorafenib, regorafenib, cabozantinib, ramucirumab -
and have marginal impact in terms of response as per Recist 1.1 [10-14] .
Further, another issue comes from the inter-observer variability in tumor response assessment per Recist 1.1
and mRecist for HCC. However, although it remains poorly known and warrants prospective assessment, it
is possible that concordance is good between operators with expertise in liver imaging and lower with non-
[15]
specifically trained operator, independently of the response criteria .
[16]
As detailed in Table 1, in ORR assessed by Recist 1.1, atezolizumab/bevacizumab and nivolumab/
[8]
ipilumumab combinations displayed the best ORR (27% and 32%, respectively), followed by lenvatinib/
[11]
TKI (18.8%) , ICI monotherapy with pembrolizumab (17%-18.3%) [17,18] and nivolumab (15%-19%) [19,20] ,
[12]
and at a disappointing lower level all the remaining TKIs such as sorafenib (2%-6.5%) [10,11] , regorafenib (7%)
and cabozantinib (4%) , and finally the monoclonal antibody ramucirumab (5%) . These data suggest
[14]
[13]
that these latter drugs have mostly a tumor-static rather than tumoricidal activity by comparison to the