Page 61 - Read Online
P. 61
Jiang et al. Hepatoma Res 2019;5:5 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.97 Page 5 of 11
(n = 148) (n = 146)
(n = 59) (n = 61)
N = 867 P = 0.043 P = 0.037
(n = 58) (n = 37)
(n = 151) (n = 172)
P = 0.038 P = 0.002
(n = 100) (n = 100)
(n = 109) (n = 109)
P = 0.027 P = 0.051
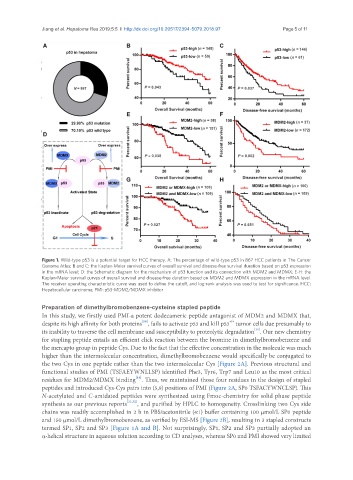
Figure 1. Wild-type p53 is a potential target for HCC therapy. A: The percentage of wild-type p53 in 867 HCC patients in The Cancer
Genome Atlas; B and C: the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of overall survival and disease-free survival duration based on p53 expression
in the mRNA level; D: the Schematic diagram for the mechanism of p53 function and its connection with MDM2 and MDMX; E-H: the
Kaplan-Meier survival curves of overall survival and disease-free duration based on MDM2 and MDMX expression in the mRNA level.
The receiver operating characteristic curve was used to define the cutoff, and log-rank analysis was used to test for significance. HCC:
Hepatocellular carcinoma; PMI: p53-MDM2/MDMX inhibitor
Preparation of dimethylbromobenzene-cysteine stapled peptide
In this study, we firstly used PMI-a potent dodecameric peptide antagonist of MDM2 and MDMX that,
+/+
[14]
despite its high affinity for both proteins , fails to activate p53 and kill p53 tumor cells due presumably to
[30]
its inability to traverse the cell membrane and susceptibility to proteolytic degradation . Our new chemistry
for stapling peptide entails an efficient click reaction between the bromine in dimethylbromobenzene and
the mercapto group in peptide Cys. Due to the fact that the effective concentration in the molecule was much
higher than the intermolecular concentration, dimethylbromobenzene would specifically be conjugated to
the two Cys in one peptide rather than the two intermolecular Cys [Figure 2A]. Previous structural and
functional studies of PMI (TSFAEYWNLLSP) identified Phe3, Tyr6, Trp7 and Leu10 as the most critical
[14]
residues for MDM2/MDMX binding . Thus, we maintained those four residues in the design of stapled
peptides and introduced Cys-Cys pairs into (5,9) positions of PMI (Figure 2A, SP0 TSFACYWNCLSP). This
N-acetylated and C-amidated peptides were synthesized using Fmoc-chemistry for solid phase peptide
synthesis as our previous reports [31,32] , and purified by HPLC to homogeneity. Crosslinking two Cys side
chains was readily accomplished in 2 h in PBS/acetonitrile (4:1) buffer containing 100 μmol/L SP0 peptide
and 150 μmol/L dimethylbromobenzene, as verified by ESI-MS [Figure 2B], resulting in 3 stapled constructs
termed SP1, SP2 and SP3 [Figure 1A and B]. Not surprisingly, SP1, SP2 and SP3 partially adopted an
α-helical structure in aqueous solution according to CD analyses, whereas SP0 and PMI showed very limited