Page 72 - Read Online
P. 72
Page 4 of 6 Buonfiglioli et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:6 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2017.42
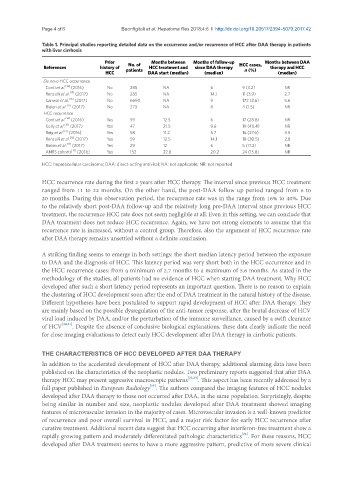
Table 1. Principal studies reporting detailed data on the occurrence and/or recurrence of HCC after DAA therapy in patients
with liver cirrhosis
Prior No. of Months between Months of follow-up HCC cases, Months between DAA
References history of patients HCC treatment and since DAA therapy n (%) therapy and HCC
HCC DAA start (median) (median) (median)
De novo HCC occurrence
Conti et al. [14] (2016) No 285 NA 6 9 (3.2) NR
[15]
Renzulli et al. (2017) No 285 NA 14.1 11 (3.9) 2.7
Kanwal et al. [16] (2017) No 6690 NA 9 172 (2.6) 5.6
Bielen et al. (2017) No 273 NA 6 4 (1.5) NR
[17]
HCC recurrence
Conti et al. [14] (2016) Yes 59 12.5 6 17 (28.8) NR
Kolly et al. [18] (2017) Yes 47 21.5 9.6 19 (40.4) NR
[13]
Reig et al. (2016) Yes 58 11.2 5.7 16 (27.6) 3.5
Renzulli et al. (2017) Yes 59 12.5 14.1 18 (30.5) 2.8
[15]
[17]
Bielen et al. (2017) Yes 29 12 6 5 (17.2) NR
ANRS cohorts [19] (2016) Yes 152 22.8 20.2 24 (15.8) NR
HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; DAA: direct-acting antiviral; NA: not applicable; NR: not reported
HCC recurrence rate during the first 2 years after HCC therapy. The interval since previous HCC treatment
ranged from 11 to 22 months. On the other hand, the post-DAA follow up period ranged from 6 to
20 months. During this observation period, the recurrence rate was in the range from 16% to 40%. Due
to the relatively short post-DAA follow-up and the relatively long pre-DAA interval since previous HCC
treatment, the recurrence HCC rate does not seem negligible at all. Even in this setting, we can conclude that
DAA treatment does not reduce HCC recurrence. Again, we have not strong elements to assume that the
recurrence rate is increased, without a control group. Therefore, also the argument of HCC recurrence rate
after DAA therapy remains unsettled without a definite conclusion.
A striking finding seems to emerge in both settings: the short median latency period between the exposure
to DAA and the diagnosis of HCC. This latency period was very short both in the HCC occurrence and in
the HCC recurrence cases: from a minimum of 2.7 months to a maximum of 5.6 months. As stated in the
methodology of the studies, all patients had no evidence of HCC when starting DAA treatment. Why HCC
developed after such a short latency period represents an important question. There is no reason to explain
the clustering of HCC development soon after the end of DAA treatment in the natural history of the disease.
Different hypotheses have been postulated to support rapid development of HCC after DAA therapy. They
are mainly based on the possible dysregulation of the anti-tumor response, after the brutal decrease of HCV
viral load induced by DAA, and/or the perturbation of the immune surveillance, caused by a swift clearance
of HCV [20,21] . Despite the absence of conclusive biological explanations, these data clearly indicate the need
for close imaging evaluations to detect early HCC development after DAA therapy in cirrhotic patients.
THE CHARACTERISTICS OF HCC DEVELOPED AFTER DAA THERAPY
In addition to the accelerated development of HCC after DAA therapy, additional alarming data have been
published on the characteristics of the neoplastic nodules. Two preliminary reports suggested that after DAA
therapy HCC may present aggressive macroscopic patterns [22,23] . This aspect has been recently addressed by a
[15]
full paper published in European Radiology . The authors compared the imaging features of HCC nodules
developed after DAA therapy to those not occurred after DAA, in the same population. Surprisingly, despite
being similar in number and size, neoplastic nodules developed after DAA treatment showed imaging
features of microvascular invasion in the majority of cases. Microvascular invasion is a well-known predictor
of recurrence and poor overall survival in HCC, and a major risk factor for early HCC recurrence after
curative treatment. Additional recent data suggest that HCC occurring after interferon-free treatment show a
[24]
rapidly growing pattern and moderately differentiated pathologic characteristics . For these reasons, HCC
developed after DAA treatment seems to have a more aggressive pattern, predictive of more severe clinical