Page 297 - Read Online
P. 297
Page 4 of 7 Tian et al. Hepatoma Res 2018;4:27 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2018.24
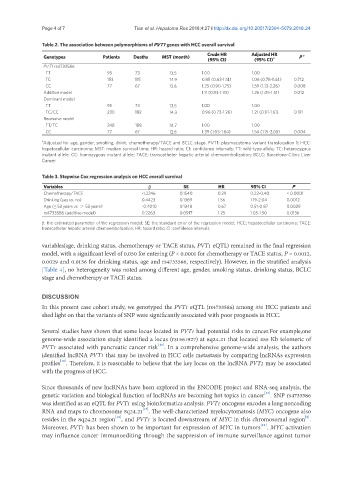
Table 2. The association between polymorphisms of PVT1 genes with HCC overall survival
Crude HR Adjusted HR a
Genotypes Patients Deaths MST (month) a P
(95% CI) (95% CI)
PVT1 rs4733586
TT 95 73 13.5 1.00 1.00
TC 153 115 14.9 0.85 (0.63-1.14) 1.06 (0.78-1.44) 0.712
CC 77 67 12.6 1.25 (0.90-1.75) 1.59 (1.13-2.26) 0.008
Additive model 1.11 (0.93-1.33) 1.26 (1.05-1.51) 0.012
Dominant model
TT 95 73 13.5 1.00 1.00
TC/CC 230 182 14.3 0.96 (0.73-1.26) 1.21 (0.91-1.61) 0.191
Recessive model
TT/TC 248 188 14.7 1.00 1.00
CC 77 67 12.6 1.39 (1.05-1.84) 1.54 (1.15-2.05) 0.004
a Adjusted for age, gender, smoking, drink, chemotherapy/TACE and BCLC stage. PVT1: plasmacytoma variant translocation 1; HCC:
hepatocellular carcinoma; MST: median survival time; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence intervals; TT: wild-type allele; TC: heterozygous
mutant allele; CC: homozygous mutant allele; TACE: transcatheter hepatic arterial chemoembolization; BCLC: Barcelona-Clinic Liver
Cancer
Table 3. Stepwise Cox regression analysis on HCC overall survival
Variables b SE HR 95% CI P
Chemotherapy/TACE -1.2246 0.1540 0.29 0.22-0.40 < 0.0001
Drinking (yes vs. no) 0.4423 0.1369 1.56 1.19-2.04 0.0012
Age (≤ 53 years vs. > 53 years) -0.4010 0.1348 0.67 0.51-0.87 0.0029
rs4733586 (additive model) 0.2263 0.0917 1.25 1.05-1.50 0.0136
b: the estimated parameter of the regression model; SE: the standard error of the regression model; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; TACE:
transcatheter hepatic arterial chemoembolization; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence intervals
variables(age, drinking status, chemotherapy or TACE status, PVT1 eQTL) remained in the final regression
model, with a significant level of 0.050 for entering (P < 0.0001 for chemotherapy or TACE status, P = 0.0012,
0.0029 and 0.0136 for drinking status, age and rs4733586, respectively). However, in the stratified analysis
[Table 4], no heterogeneity was noted among different age, gender, smoking status, drinking status, BCLC
stage and chemotherapy or TACE status.
DISCUSSION
In this present case cohort study, we genotyped the PVT1 eQTL (rs4733586) among 331 HCC patients and
shed light on that the variants of SNP were significantly associated with poor prognosis in HCC.
Several studies have shown that some locus located in PVT1 had potential risks to cancer.For example,one
genome-wide association study identified a locus (rs1561927) at 8q24.21 that located 455 Kb telomeric of
[15]
PVT1 associated with pancreatic cancer risk . In a comprehensive genome-wide analysis, the authors
identified lncRNA PVT1 that may be involved in HCC cells metastasis by comparing lncRNAs expression
[16]
profiles . Therefore, it is reasonable to believe that the key locus on the lncRNA PVT1 may be associated
with the progress of HCC.
Since thousands of new lncRNAs have been explored in the ENCODE project and RNA-seq analysis, the
[12]
genetic variation and biological function of lncRNAs are becoming hot topics in cancer . SNP rs4733586
was identified as an eQTL for PVT1 using bioinformatics analysis. PVT1 oncogene encodes a long noncoding
[17]
RNA and maps to chromosome 8q24.21 . The well-characterized myelocytomatosis (MYC) oncogene also
[9]
[18]
resides in the 8q24.21 region , and PVT1 is located downstream of MYC in this chromosomal region .
[19]
Moreover, PVT1 has been shown to be important for expression of MYC in tumors . MYC activation
may influence cancer immunoediting through the suppression of immune surveillance against tumor