Page 30 - Read Online
P. 30
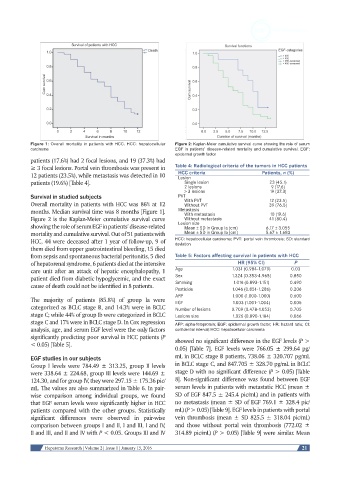
Figure 1: Overall mortality in patients with HCC. HCC: hepatocellular Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival curve showing the role of serum
carcinoma EGF in patients’ disease-related mortality and cumulative survival. EGF:
epidermal growth factor
patients (17.6%) had 2 focal lesions, and 19 (37.3%) had
≥ 3 focal lesions. Portal vein thrombosis was present in Table 4: Radiological criteria of the tumors in HCC patients
12 patients (23.5%), while metastasis was detected in 10 HCC criteria Patients, n (%)
Lesion
patients (19.6%) [Table 4]. Single lesion 23 (45.1)
2 lesions 9 (17.6)
> 3 lesions 19 (37.3)
Survival in studied subjects PVT
Overall mortality in patients with HCC was 86% at 12 With PVT 12 (23.5)
Without PVT
39 (76.5)
months. Median survival time was 8 months [Figure 1]. Metastasis 10 (19.6)
With metastasis
Figure 2 is the Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival curve Without metastasis 41 (80.4)
showing the role of serum EGF in patients’ disease-related Lesion size 6.17 ± 3.055
Mean ± SD in Group Ia (cm)
mortality and cumulative survival. Out of 51 patients with Mean ± SD in Group Ib (cm) 5.67 ± 1.683
HCC, 44 were deceased after 1 year of follow-up, 9 of HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; PVT: portal vein thrombosis; SD: standard
deviation
them died from upper gastrointestinal bleeding, 15 died
from sepsis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, 5 died Table 5: Factors affecting survival in patients with HCC
of hepatorenal syndrome, 6 patients died at the intensive HR (95% CI) P
care unit after an attack of hepatic encephalopathy, 1 Age 1.031 (0.984-1.079) 0.03
patient died from diabetic hypoglycemic, and the exact Sex 1.324 (0.353-4.965) 0.850
cause of death could not be identified in 8 patients. Smoking 1.014 (0.893-1.151) 0.490
Pesticide 1.046 (0.851-1.286) 0.206
AFP 1.000 (1.000-1.000) 0.600
The majority of patients (85.8%) of group Ia were EGF 1.003 (1.001-1.004) 0.005
categorized as BCLC stage B, and 14.3% were in BCLC Number of lesions 0.709 (0.478-1.053) 0.705
stage C; while 44% of group Ib were categorized in BCLC Lesions size 1.026 (0.890-1.184) 0.066
stage C and 17% were in BCLC stage D. In Cox regression AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; EGF: epidermal growth factor; HR: hazard ratio; CI:
analysis, age, and serum EGF level were the only factors confidential interval; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
significantly predicting poor survival in HCC patients (P showed no significant difference in the EGF levels (P >
< 0.05) [Table 5].
0.05) [Table 7]. EGF levels were 766.05 ± 299.64 pg/
EGF studies in our subjects mL in BCLC stage B patients, 738.06 ± 320.707 pg/mL
Group I levels were 784.49 ± 313.25, group II levels in BCLC stage C, and 847.705 ± 328.70 pg/mL in BCLC
were 338.64 ± 224.68, group III levels were 144.69 ± stage D with no significant difference (P > 0.05) [Table
124.30, and for group IV, they were 297.15 ± 175.36 pic/ 8]. Non-significant difference was found between EGF
mL. The values are also summarized in Table 6. In pair- serum levels in patients with metastatic HCC (mean ±
wise comparison among individual groups, we found SD of EGF 847.5 ± 245.4 pic/mL) and in patients with
that EGF serum levels were significantly higher in HCC no metastasis (mean ± SD of EGF 769.1 ± 328.4 pic/
patients compared with the other groups. Statistically mL) (P > 0.05) [Table 9]. EGF levels in patients with portal
significant differences were observed in pair-wise vein thrombosis (mean ± SD 825.5 ± 318.04 pic/mL)
comparison between groups I and II, I and III, I and IV, and those without portal vein thrombosis (772.02 ±
II and III, and II and IV with P < 0.05. Groups III and IV 314.89 pic/mL) (P > 0.05) [Table 9] were similar. Mean
Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | Issue 1 | January 15, 2016 21