Page 217 - Read Online
P. 217
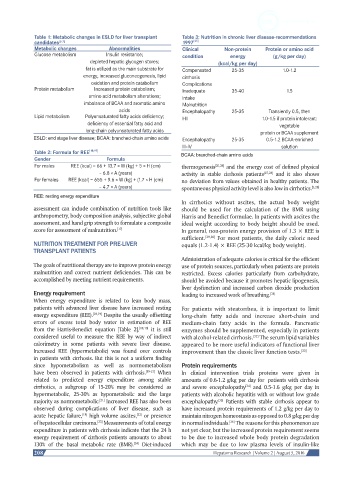
Table 1: Metabolic changes in ESLD for liver transplant Table 3: Nutrition in chronic liver disease-recommendations
candidates [5-7] 1997 [45]
Metabolic changes Abnormalities Clinical Non-protein Protein or amino acid
Glucose metabolism Insulin resistance; condition energy (g/kg per day)
depleted hepatic glycogen stores; (kcal/kg per day)
fat is utilized as the main substrate for Compensated 25-35 1.0-1.2
energy, increased gluconeogenesis, lipid cirrhosis
oxidation and protein catabolism Complications
Protein metabolism Increased protein catabolism; Inadequate 35-40 1.5
amino acid metabolism alterations; intake
imbalance of BCAA and aromatic amino Malnutrition
acids Encephalopathy 25-35 Transiently 0.5, then
Lipid metabolism Polyunsaturated fatty acids deficiency; I-II 1.0-1.5 if protein intolerant:
deficiency of essential fatty acid and vegetable
long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids protein or BCAA supplement
ESLD: end stage liver disease; BCAA: branched-chain amino acids Encephalopathy 25-35 0.5-1.2 BCAA-enriched
III-IV solution
Table 2: Formula for REE [18,19] BCAA: branched-chain amino acids
Gender Formula
For males REE (kcal) = 66 + 13.7 × W (kg) + 5 × H (cm) thermogenesis [25,26] and the energy cost of defined physical
– 6.8 × A (years) activity in stable cirrhosis patients [27,28] and it also shows
For females REE (kcal) = 655 + 9.6 × W (kg) + (1.7 × H (cm) no deviation from values obtained in healthy patients. The
– 4.7 × A (years) spontaneous physical activity level is also low in cirrhotics. [5,28]
REE: resting energy expenditure
In cirrhotics without ascites, the actual body weight
assessment can include combination of nutrition tools like should be used for the calculation of the BMR using
anthropometry, body composition analysis, subjective global Harris and Benedict formulae. In patients with ascites the
assessment, and hand grip strength to formulate a composite ideal weight according to body height should be used.
score for assessment of malnutrition. [17] In general, non-protein energy provision of 1.3 × REE is
sufficient. [29,30] For most patients, the daily caloric need
NUTRITION TREATMENT FOR PRE-LIVER equals (1.2-1.4) × REE (25-30 kcal/kg body weight).
TRANSPLANT PATIENTS
Administration of adequate calories is critical for the efficient
The goals of nutritional therapy are to improve protein energy use of protein sources, particularly when patients are protein
malnutrition and correct nutrient deficiencies. This can be restricted. Excess calories particularly from carbohydrate,
accomplished by meeting nutrient requirements. should be avoided because it promotes hepatic lipogenesis,
liver dysfunction and increased carbon dioxide production
Energy requirement leading to increased work of breathing.
[31]
When energy expenditure is related to lean body mass,
patients with advanced liver disease have increased resting For patients with steatorrhea, it is important to limit
energy expenditure (REE). [18,19] Despite the usually offsetting long-chain fatty acids and increase short-chain and
errors of excess total body water in estimation of REE medium-chain fatty acids in the formula. Pancreatic
from the Harris-Benedict equation [Table 2], [18,19] it is still enzymes should be supplemented, especially in patients
considered useful to measure the REE by way of indirect with alcohol-related cirrhosis. The serum lipid variables
[32]
calorimetry in some patients with severe liver disease. appeared to be more useful indicators of functional liver
Increased REE (hypermetabolic) was found over controls improvement than the classic liver function tests. [33]
in patients with cirrhosis. But this is not a uniform finding
since hypometabolism as well as normometabolism Protein requirements
have been observed in patients with cirrhosis. [19-21] When In clinical intervention trials proteins were given in
related to predicted energy expenditure among stable amounts of 0.6-1.2 g/kg per day for patients with cirrhosis
cirrhotics, a subgroup of 15-20% may be considered as and severe encephalopathy and 0.5-1.6 g/kg per day in
[34]
hypermetabolic, 25-30% as hypometabolic and the large patients with alcoholic hepatitis with or without low grade
majority as normometabolic. Increased REE has also been encephalopathy. Patients with stable cirrhosis appear to
[35]
[21]
observed during complications of liver disease, such as have increased protein requirements of 1.2 g/kg per day to
acute hepatic failure, high volume ascites, or presence maintain nitrogen homeostasis as opposed to 0.8 g/kg per day
[18]
[22]
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Measurements of total energy in normal individuals. The reasons for this phenomenon are
[36]
[23]
expenditure in patients with cirrhosis indicate that the 24 h not yet clear, but the increased protein requirement seems
energy requirement of cirrhosis patients amounts to about to be due to increased whole body protein degradation
130% of the basal metabolic rate (BMR). Diet-induced which may be due to low plasma levels of insulin-like
[24]
208 Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | August 5, 2016