Page 178 - Read Online
P. 178
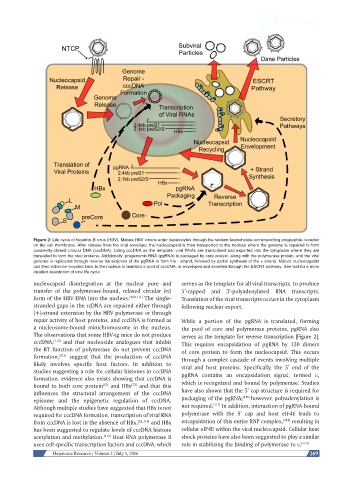
Figure 2: Life cycle of hepatitis B virus (HBV). Mature HBV virions enter hepatocytes through the sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide receptor
on the cell membrane. After release from the viral envelope, the nucleocapsid is then transported to the nucleus where the genome is repaired to form
covalently-closed circular DNA (cccDNA). Using cccDNA as the template, viral RNAs are transcribed and exported into the cytoplasm where they are
translated to form the viral proteins. Additionally, pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) is packaged by core protein, along with the polymerase protein, and the viral
genome is replicated through reverse transcription of the pgRNA to form the - strand, followed by partial synthesis of the + strand. Mature nucleocapsids
can then either be recycled back to the nucleus to maintain a pool of cccDNA, or enveloped and secreted through the ESCRT pathway. See text for a more
detailed description of viral life cycle
nucleocapsid disintegration at the nuclear pore and serves as the template for all viral transcripts, to produce
transfer of the polymerase-bound, relaxed circular (rc) 5’-capped and 3’-polyadenylated RNA transcripts.
form of the HBV DNA into the nucleus. [110,111] The single- Translation of the viral transcripts occurs in the cytoplasm
stranded gaps in the rcDNA are repaired either through following nuclear export.
(+)-strand extension by the HBV polymerase or through
repair activity of host proteins, and cccDNA is formed as While a portion of the pgRNA is translated, forming
a nucleosome-bound minichromosome in the nucleus. the pool of core and polymerase proteins, pgRNA also
The observations that some HBV-tg mice do not produce serves as the template for reverse transcription [Figure 2].
cccDNA, [112] and that nucleoside analogues that inhibit This requires encapsidation of pgRNA by 120 dimers
the RT function of polymerase do not prevent cccDNA of core protein to form the nucleocapsid. This occurs
formation, [113] suggest that the production of cccDNA through a complex cascade of events involving multiple
likely involves specific host factors. In addition to viral and host proteins. Specifically, the 5’ end of the
studies suggesting a role for cellular histones in cccDNA
formation, evidence also exists showing that cccDNA is pgRNA contains an encapsidation signal, termed ε,
bound to both core protein and HBx and that this which is recognized and bound by polymerase. Studies
[73]
[53]
influences the structural arrangement of the cccDNA have also shown that the 5’ cap structure is required for
episome and the epigenetic regulation of cccDNA. packaging of the pgRNA; [116] however, polyadenylation is
Although multiple studies have suggested that HBx is not not required. [117] In addition, interaction of pgRNA-bound
required for cccDNA formation, transcription of viral RNA polymerase with the 5’ cap and host eIF4E leads to
from cccDNA is lost in the absence of HBx, [28,114] and HBx encapsidation of this entire RNP complex, [118] resulting in
has been suggested to regulate levels of cccDNA histone cellular eIF4E within the viral nucleocapsid. Cellular heat
acetylation and methylation. [115] Host RNA polymerase II shock proteins have also been suggested to play a similar
uses cell-specific transcription factors and cccDNA, which role in stabilizing the binding of polymerase to ε. [119]
Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | July 1, 2016 169