Page 43 - Read Online
P. 43
Robichaux et al. LLR in the cirrhotic patient
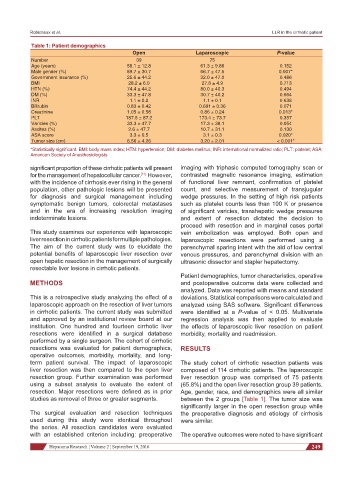
Table 1: Patient demographics
Open Laparoscopic P-value
Number 39 75
Age (years) 58.1 ± 12.8 61.3 ± 9.86 0.152
Male gender (%) 89.7 ± 30.7 66.7 ± 47.5 0.007*
Government insurance (%) 25.6 ± 44.2 32.0 ± 47.0 0.486
BMI 28.2 ± 6.0 27.8 ± 4.9 0.713
HTN (%) 74.4 ± 44.2 80.0 ± 40.3 0.494
DM (%) 33.3 ± 47.8 30.7 ± 40.2 0.664
INR 1.1 ± 0.2 1.1 ± 0.1 0.638
Bilirubin 0.83 ± 0.42 0.691 ± 0.36 0.071
Creatinine 1.05 ± 0.58 0.86 ± 0.24 0.013*
PLT 187.5 ± 87.2 173.4 ± 73.7 0.357
Varicies (%) 33.3 ± 47.7 17.3 ± 38.1 0.054
Ascites (%) 2.6 ± 47.7 10.7 ± 31.1 0.130
ASA score 3.3 ± 0.5 3.1 ± 0.3 0.020*
Tumor size (cm) 6.56 ± 4.26 3.20 ± 2.01 < 0.001*
*Statistically significant. BMI: body mass index; HTN: hypertension; DM: diabetes mellitus; INR: international normalized ratio; PLT: platelet; ASA:
American Society of Anesthesiologists
significant proportion of these cirrhotic patients will present imaging with triphasic computed tomography scan or
for the management of hepatocellular cancer. However, contrasted magnetic resonance imaging, estimation
[11]
with the incidence of cirrhosis ever rising in the general of functional liver remnant, confirmation of platelet
population, other pathologic lesions will be presented count, and selective measurement of transjugular
for diagnosis and surgical management including wedge pressures. In the setting of high risk patients
symptomatic benign tumors, colorectal metastases such as platelet counts less than 100 K or presence
and in the era of increasing resolution imaging of significant varicies, transhepatic wedge pressures
indeterminate lesions. and extent of resection dictated the decision to
proceed with resection and in marginal cases portal
This study examines our experience with laparoscopic vein embolization was employed. Both open and
liver resection in cirrhotic patients for multiple pathologies. laparoscopic resections were performed using a
The aim of the current study was to elucidate the parenchymal sparing intent with the aid of low central
potential benefits of laparoscopic liver resection over venous pressures, and parenchymal division with an
open hepatic resection in the management of surgically ultrasonic dissector and stapler hepatectomy.
resectable liver lesions in cirrhotic patients.
Patient demographics, tumor characteristics, operative
METHODS and postoperative outcome data were collected and
analyzed. Data was reported with means and standard
This is a retrospective study analyzing the effect of a deviations. Statistical comparisons were calculated and
laparoscopic approach on the resection of liver tumors analyzed using SAS software. Significant differences
in cirrhotic patients. The current study was submitted were identified at a P-value of < 0.05. Multivariate
and approved by an institutional review board at our regression analysis was then applied to evaluate
institution. One hundred and fourteen cirrhotic liver the effects of laparoscopic liver resection on patient
resections were identified in a surgical database morbidity, mortality and readmission.
performed by a single surgeon. The cohort of cirrhotic
resections was evaluated for patient demographics, RESULTS
operative outcomes, morbidity, mortality, and long-
term patient survival. The impact of laparoscopic The study cohort of cirrhotic resection patients was
liver resection was then compared to the open liver composed of 114 cirrhotic patients. The laparoscopic
resection group. Further examination was performed liver resection group was comprised of 75 patients
using a subset analysis to evaluate the extent of (65.8%) and the open liver resection group 39 patients.
resection. Major resections were defined as in prior Age, gender, race, and demographics were all similar
studies as removal of three or greater segments. between the 2 groups [Table 1]. The tumor size was
significantly larger in the open resection group while
The surgical evaluation and resection techniques the preoperative diagnosis and etiology of cirrhosis
used during this study were identical throughout were similar.
the series. All resection candidates were evaluated
with an established criterion including: preoperative The operative outcomes were noted to have significant
Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 2 ¦ September 19, 2016 249